Scale Cluster
In Zilliz Cloud, a query CU is a set of hardware resources used to serve indexes and process search requests. You can think of a query CU as a fully managed physical node that runs your query service. A replica is a cluster-level copy that contains the same resources and data. Query CUs primarily determine cluster capacity and compute resources, while replicas provide additional parallelism for serving queries.
Query CU vs Replica
As your workload grows and more data is written, a cluster may eventually reach its capacity and performance limit. To proactively manage this, you can monitor Query CU Capacity and Query CU Computation on the metrics page and scale before you hit the limit.
Choosing whether to scale query CUs or replicas depends on your goal. As a rule of thumb:
-
For clusters with 1 - 8 query CUs, you can directly scale query CU.
-
For clusters with more than 8 query CUs, you can scale query CU or replica depending on your need.
Scale query CUs for more capacity
Scale query CUs if you are hitting capacity-related limits or expect continued growth in data and workload.
Typical signals and scenarios include:
-
Write operations fail while reads still succeed. This often indicates the cluster is at or near capacity.
-
You are working with large datasets or require more collections.
-
You are seeing high CPU or memory usage.
For details, see Scale Query CU.
Scale replicas for higher throughput or availability
Scale replicas when your cluster can hold the data, but you see bottlenecks of query throughput (QPS) or need better availability.
Typical signals and scenarios include:
-
Small-to-medium datasets, but you experience QPS bottlenecks.
-
You want to distribute query load across multiple identical copies to increase throughput.
-
You want improved availability.
For details, see Scale Replica.
Scaling options
Zilliz Cloud provides multiple ways to scale cluster resources. Depending on your workload pattern, you can scale immediately, on a schedule, or automatically.
Manual scaling
Manually adjust resources when you have a clear understanding of your workload and can predict when changes are needed.
-
Query CUs: Increase to expand capacity; decrease to reduce cost when demand drops.
-
Replicas: Increase to raise query throughput and availability; decrease when demand drops.
Scheduled scaling
Use scheduled scaling when your workload has recurring patterns (for example, weekday peaks and weekend troughs). Common use cases include business-hours traffic spikes and predictable batch/query windows.
For scheduled scaling, Zilliz Cloud provides 2 modes:
-
Basic mode: A simple selector to define schedule
-
Advanced mode: Use Unix cron expressions for greater flexibility.
Dynamic scaling
Enable dynamic scaling for unpredictable workloads. Zilliz Cloud automatically adjusts resources within a user-defined min–max range based on real-time metrics.
-
Query CUs: Auto-scales based on the CU Capacity metric value.
-
Replicas: Auto-scales based on the CU Computation metric value.
FAQs
-
Which scaling option should I choose?
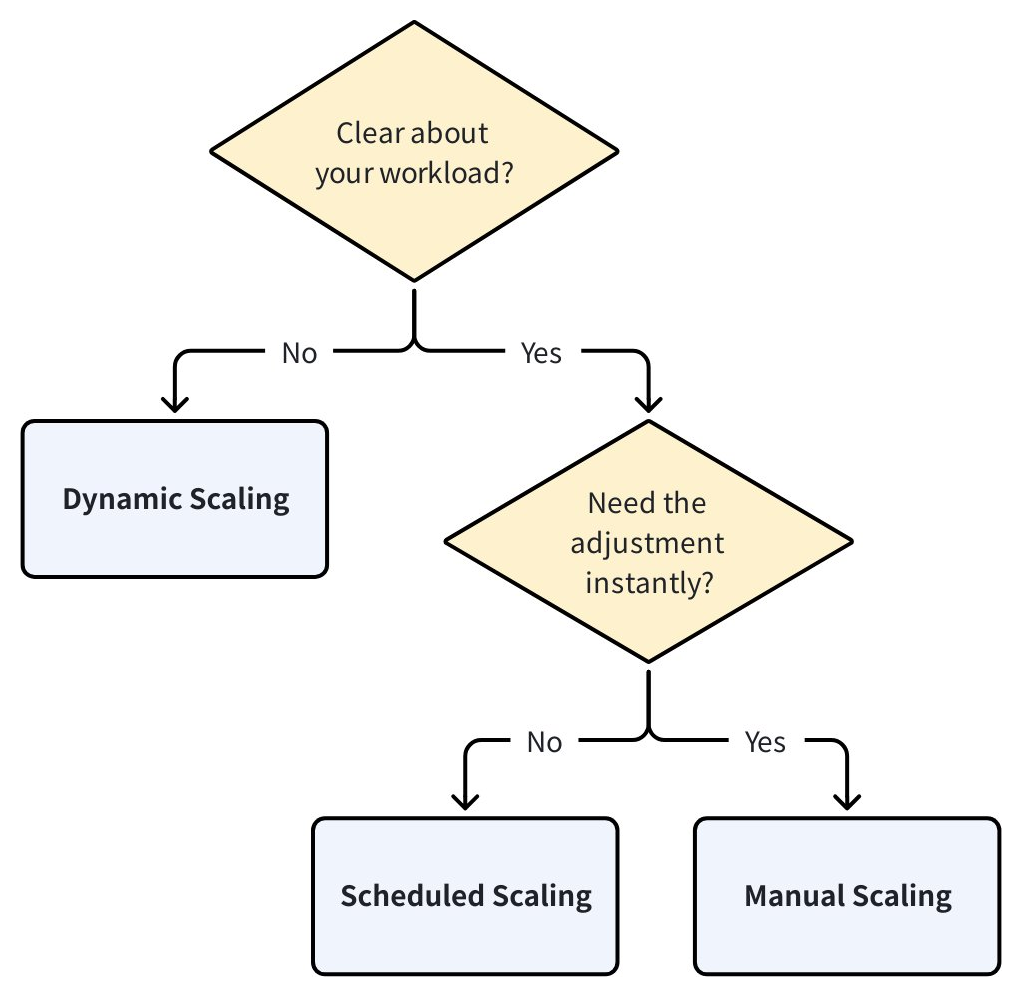
The following is a quick tip to help you choose the right scaling method for your needs:
-
If you have a very clear understanding of your workload patterns—such as consistent daily peaks or planned batch import jobs—manual scaling and scheduled scaling is right option for you. If you need to adjust the query CU immediately, choose manual scaling. If you want the adjustment to occur recurringly at a specific future time, choose scheduled scaling.
-
If your workload is unpredictable and varies throughout the day or week, dynamic scaling is recommended. It adjusts the cluster size automatically within a range you define, helping to maintain performance while optimizing cost.
-
-
When should I scale replicas and when should I scale query CU?
You are recommended to:
-
Increase replica count when:
-
You need to handle high QPS (queries per second) and high availability.
-
Your workload consists of many concurrent search or query requests. You need to increase throughput.
Tips: Each replica is an independent copy of the query CU resources and handles a subset of queries.
-
-
Increase query CU when:
-
You are working with large datasets or require more collections.
-
You are seeing high CPU or memory usage.
Tips: Increasing CU size gives each query node more computing resources and capacity.
-
-
Suggestion: For clusters with 1 - 8 CUs, you can directly scale query CU. For clusters with more than 8 CUs, please increase replicas.
-
-
How does scaling work in Zilliz Cloud?
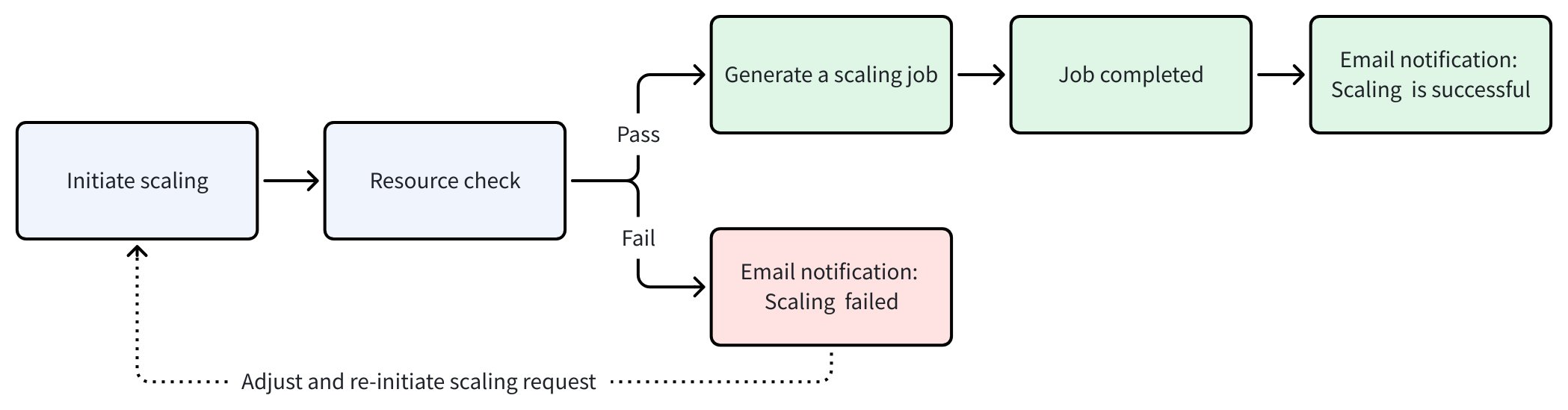
The following diagram shows the workflow of a scaling operation in Zilliz Cloud.
-
Initiate scaling: You can submit a scaling request via the web console or through the RESTful API.
-
Resource check: Zilliz Cloud validates your scaling request against the following requirements.
-
Enterprise project: Query CU × Replica ≤ 256
-
Standard project: Query CU × Replica ≤ 32
-
If Replica > 1, the cluster cannot scale down to less than 8 query CUs.
-
Current data volume < 80% of the CU capacity of the new CU size.
-
Current number of collections and partitions < the maximum number of collections and partitions allowed in the new CU size.
-
If you have any problems with scaling, contact support.
-
-
Generate a scaling job: Once the resource check passes, Zilliz Cloud creates a scaling job. You can track progress on the Jobs page. During this time, the cluster status changes to Modifying, and cluster operations such as suspend, migrate, and drop are unavailable.
-
Job completed: When the job completes, scaling succeeds and the cluster status returns to Running. You will also receive an email confirming the resource adjustment.
-
Scale Query CU [READ MORE]
As your workload grows and more data is written, the cluster may reach its capacity limit. In such cases, read operations will continue to function, but new write operations may fail.
Scale Replica [READ MORE]
Zilliz Cloud supports cluster-level replication. Each replica is an exact copy of the resources and data in a cluster. Using replicas can increase query throughput and availability.
Cron Expression [READ MORE]
A cron expression defines a schedule for running a scaling task at specific times.