Multi-language Analyzers
When Zilliz Cloud performs text analysis, it typically applies a single analyzer across an entire text field in a collection. If that analyzer is optimized for English, it struggles with the very different tokenization and stemming rules required by other languages, such as Chinese, Spanish, or French, resulting a lower recall rate. For instance, a search for the Spanish word "teléfono" (meaning "phone") would trip up an English‑focused analyzer: it may drop the accent and apply no Spanish‑specific stemming, causing relevant results to be overlooked.
Multi‑language analyzers resolve this issue by allowing you to configure multiple analyzers for a text field in a single collection. This way, you can store multilingual documents in a text field, and Zilliz Cloud analyzes text according to the appropriate language rules for each document.
Limits
-
This feature works only with BM25-based text retrieval and sparse vectors. For more information, refer to Full Text Search.
-
Each document in a single collection can use only one analyzer, determined by its language identifier field value.
-
Performance may vary depending on the complexity of your analyzers and the size of your text data.
Overview
The following diagram shows the workflow of configuring and using multi-language analyzers in Zilliz Cloud:
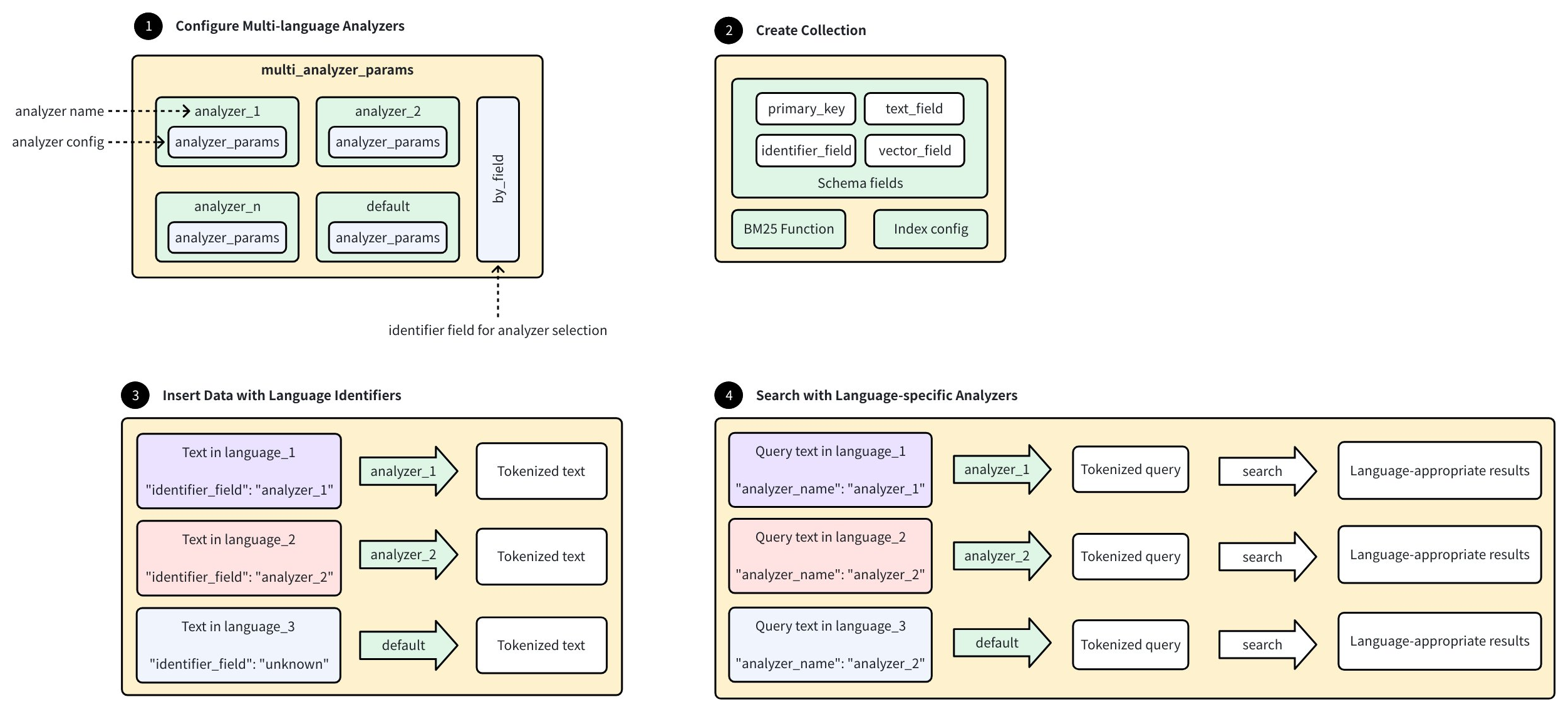
-
Configure Multi-language Analyzers:
-
Set up multiple language-specific analyzers using the format:
<analyzer_name>: <analyzer_config>, where eachanalyzer_configfollows standardanalyzer_paramsconfiguration as described in Analyzer Overview. -
Define a special identifier field that will determine analyzer selection for each document.
-
Configure a
defaultanalyzer for handling unknown languages.
-
-
Create Collection:
-
Define schema with essential fields:
-
primary_key: Unique document identifier.
-
text_field: Stores original text content.
-
identifier_field: Indicates which analyzer to use for each document.
-
vector_field: Stores sparse embeddings to be generated by the BM25 function.
-
-
Configure BM25 function and indexing parameters.
-
-
Insert Data with Language Identifiers:
-
Add documents containing text in various languages, where each document includes an identifier value specifying which analyzer to use.
-
Zilliz Cloud selects the appropriate analyzer based on the identifier field, and documents with unknown identifiers use the
defaultanalyzer.
-
-
Search with Language-Specific Analyzers:
-
Provide query text with an analyzer name specified, and Zilliz Cloud processes the query using the specified analyzer.
-
Tokenization occurs according to language-specific rules, and search returns language-appropriate results based on similarity.
-
Step 1: Configure multi_analyzer_params
The multi_analyzer_params is a single JSON object that determines how Zilliz Cloud selects the appropriate analyzer for each entity:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
multi_analyzer_params = {
# Define language-specific analyzers
# Each analyzer follows this format: <analyzer_name>: <analyzer_params>
"analyzers": {
"english": {"type": "english"}, # English-optimized analyzer
"chinese": {"type": "chinese"}, # Chinese-optimized analyzer
"default": {"tokenizer": "icu"} # Required fallback analyzer
},
"by_field": "language", # Field determining analyzer selection
"alias": {
"cn": "chinese", # Use "cn" as shorthand for Chinese
"en": "english" # Use "en" as shorthand for English
}
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("analyzers", new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("english", new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "english");
}});
put("chinese", new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "chinese");
}});
put("default", new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("tokenizer", "icu");
}});
}});
analyzerParams.put("by_field", "language");
analyzerParams.put("alias", new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("cn", "chinese");
put("en", "english");
}});
const multi_analyzer_params = {
// Define language-specific analyzers
// Each analyzer follows this format: <analyzer_name>: <analyzer_params>
"analyzers": {
"english": {"type": "english"}, # English-optimized analyzer
"chinese": {"type": "chinese"}, # Chinese-optimized analyzer
"default": {"tokenizer": "icu"} # Required fallback analyzer
},
"by_field": "language", # Field determining analyzer selection
"alias": {
"cn": "chinese", # Use "cn" as shorthand for Chinese
"en": "english" # Use "en" as shorthand for English
}
}
multiAnalyzerParams := map[string]any{
"analyzers": map[string]any{
"english": map[string]string{"type": "english"},
"chinese": map[string]string{"type": "chinese"},
"default": map[string]string{"tokenizer": "icu"},
},
"by_field": "language",
"alias": map[string]string{
"cn": "chinese",
"en": "english",
},
}
# restful
export multi_analyzer_params='{
"analyzers": {
"english": {
"type": "english"
},
"chinese": {
"type": "chinese"
},
"default": {
"tokenizer": "icu"
}
},
"by_field": "language",
"alias": {
"cn": "chinese",
"en": "english"
}
}'
Parameter | Required? | Description | Rules |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Lists every language‑specific analyzer that Zilliz Cloud can use to process text. Each analyzer in |
|
| Yes | Name of the field that stores, for every document, the language (that is, the analyzer name) Zilliz Cloud should apply. |
|
| No | Creates shortcuts or alternative names for your analyzers, making them easier to reference in your code. Each analyzer can have one or more aliases. | Each alias must map to an existing analyzer key. |
Step 2: Create collection
Creating a collection with multi-language support requires configuring specific fields and indexes:
Step 1: Add fields
In this step, define the collection schema with four essential fields:
-
Primary Key Field (
id): A unique identifier for each entity in the collection. Settingauto_id=Trueenables Zilliz Cloud to automatically generate these IDs. -
Language Indicator Field (
language): This VARCHAR field corresponds to theby_fieldspecified in yourmulti_analyzer_params. It stores the language identifier for each entity, which tells Zilliz Cloud which analyzer to use. -
Text Content Field (
text): This VARCHAR field stores the actual text data you want to analyze and search. Settingenable_analyzer=Trueis crucial as it activates text analysis capabilities for this field. Themulti_analyzer_paramsconfiguration is attached directly to this field, establishing the connection between your text data and language-specific analyzers. -
Vector Field (
sparse): This field will store the sparse vectors generated by the BM25 function. These vectors represent the analyzable form of your text data and are what Zilliz Cloud actually searches.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Import required modules
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType, Function, FunctionType
# Initialize client
client = MilvusClient(
uri="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT",
)
# Initialize a new schema
schema = client.create_schema()
# Step 2.1: Add a primary key field for unique document identification
schema.add_field(
field_name="id", # Field name
datatype=DataType.INT64, # Integer data type
is_primary=True, # Designate as primary key
auto_id=True # Auto-generate IDs (recommended)
)
# Step 2.2: Add language identifier field
# This MUST match the "by_field" value in language_analyzer_config
schema.add_field(
field_name="language", # Field name
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, # String data type
max_length=255 # Maximum length (adjust as needed)
)
# Step 2.3: Add text content field with multi-language analysis capability
schema.add_field(
field_name="text", # Field name
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, # String data type
max_length=8192, # Maximum length (adjust based on expected text size)
enable_analyzer=True, # Enable text analysis
multi_analyzer_params=multi_analyzer_params # Connect with our language analyzers
)
# Step 2.4: Add sparse vector field to store the BM25 output
schema.add_field(
field_name="sparse", # Field name
datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR # Sparse vector data type
)
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import io.milvus.common.clientenum.FunctionType;
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.DropCollectionReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.utility.request.FlushReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.InsertReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.EmbeddedText;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema collectionSchema = CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema.builder()
.build();
collectionSchema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("id")
.dataType(DataType.Int64)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.build());
collectionSchema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("language")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(255)
.build());
collectionSchema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("text")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(8192)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.multiAnalyzerParams(analyzerParams)
.build());
collectionSchema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("sparse")
.dataType(DataType.SparseFloatVector)
.build());
import { MilvusClient, DataType, FunctionType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
// Initialize client
const client = new MilvusClient({
address: "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT",
});
// Initialize schema array
const schema = [
{
name: "id",
data_type: DataType.Int64,
is_primary_key: true,
auto_id: true,
},
{
name: "language",
data_type: DataType.VarChar,
max_length: 255,
},
{
name: "text",
data_type: DataType.VarChar,
max_length: 8192,
enable_analyzer: true,
analyzer_params: multi_analyzer_params,
},
{
name: "sparse",
data_type: DataType.SparseFloatVector,
},
];
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/column"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/entity"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/index"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/milvusclient"
)
client, err := milvusclient.New(ctx, &milvusclient.ClientConfig{
Address: "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT",
APIKey: "YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN",
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
schema := entity.NewSchema()
schema.WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("id").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeInt64).
WithIsPrimaryKey(true).
WithIsAutoID(true),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("language").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).
WithMaxLength(255),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("text").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).
WithMaxLength(8192).
WithEnableAnalyzer(true).
WithMultiAnalyzerParams(multiAnalyzerParams),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("sparse").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeSparseVector),
)
# restful
export TOKEN="YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN"
export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
export idField='{
"fieldName": "id",
"dataType": "Int64",
"isPrimary": true,
"autoID": true
}'
export languageField='{
"fieldName": "language",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 255
}
}'
export textField='{
"fieldName": "text",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 8192,
"enable_analyzer": true,
"multiAnalyzerParam": '"$multi_analyzer_params"'
},
}'
export sparseField='{
"fieldName": "sparse",
"dataType": "SparseFloatVector"
}'
Step 2: Define BM25 function
Define a BM25 function to generate sparse vector representations from your raw text data:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Create the BM25 function
bm25_function = Function(
name="text_to_vector", # Descriptive function name
function_type=FunctionType.BM25, # Use BM25 algorithm
input_field_names=["text"], # Process text from this field
output_field_names=["sparse"] # Store vectors in this field
)
# Add the function to our schema
schema.add_function(bm25_function)
CreateCollectionReq.Function function = CreateCollectionReq.Function.builder()
.functionType(FunctionType.BM25)
.name("text_to_vector")
.inputFieldNames(Collections.singletonList("text"))
.outputFieldNames(Collections.singletonList("sparse"))
.build();
collectionSchema.addFunction(function);
const functions = [
{
name: "text_bm25_emb",
description: "bm25 function",
type: FunctionType.BM25,
input_field_names: ["text"],
output_field_names: ["sparse"],
params: {},
},
];
function := entity.NewFunction()
schema.WithFunction(function.WithName("text_to_vector").
WithType(entity.FunctionTypeBM25).
WithInputFields("text").
WithOutputFields("sparse"))
# restful
export function='{
"name": "text_to_vector",
"type": "BM25",
"inputFieldNames": ["text"],
"outputFieldNames": ["sparse"]
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": true,
\"fields\": [
$idField,
$languageField,
$textField,
$sparseField
],
\"functions\": [
$function
]
}"
This function automatically applies the appropriate analyzer to each text entry based on its language identifier. For more information on BM25-based text retrieval, refer to Full Text Search.
Step 3: Configure index params
To allow efficient searching, create an index on the sparse vector field:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Configure index parameters
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
# Add index for sparse vector field
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse", # Field to index (our vector field)
index_type="AUTOINDEX", # Let Milvus choose optimal index type
metric_type="BM25" # Must be BM25 for this feature
)
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("sparse")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.BM25)
.build());
const index_params = [{
field_name: "sparse",
index_type: "AUTOINDEX",
metric_type: "BM25"
}];
idx := index.NewAutoIndex(index.MetricType(entity.BM25))
indexOption := milvusclient.NewCreateIndexOption("multilingual_documents", "sparse", idx)
# restful
export IndexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "sparse",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX",
"metricType": "BM25",
"params": {}
}
]'
The index improves search performance by organizing sparse vectors for efficient BM25 similarity calculations.
Step 4: Create the collection
This final creation step brings together all your previous configurations:
-
collection_name="multilang_demo"names your collection for future reference. -
schema=schemaapplies the field structure and function you defined. -
index_params=index_paramsimplements the indexing strategy for efficient searches.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Create collection
COLLECTION_NAME = "multilingual_documents"
# Check if collection already exists
if client.has_collection(COLLECTION_NAME):
client.drop_collection(COLLECTION_NAME) # Remove it for this example
print(f"Dropped existing collection: {COLLECTION_NAME}")
# Create the collection
client.create_collection(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME, # Collection name
schema=schema, # Our multilingual schema
index_params=index_params # Our search index configuration
)
client.dropCollection(DropCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("multilingual_documents")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("multilingual_documents")
.collectionSchema(collectionSchema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
const COLLECTION_NAME = "multilingual_documents";
// Create the collection
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
schema: schema,
index_params: index_params,
functions: functions
});
err = client.CreateCollection(ctx,
milvusclient.NewCreateCollectionOption("multilingual_documents", schema).
WithIndexOptions(indexOption))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
# restful
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{
\"collectionName\": \"multilingual_documents\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $IndexParams
}"
At this point, Zilliz Cloud creates an empty collection with multi-language analyzer support, ready to receive data.
Step 3: Insert example data
When adding documents to your multi-language collection, each must include both text content and a language identifier:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Prepare multilingual documents
documents = [
# English documents
{
"text": "Artificial intelligence is transforming technology",
"language": "english", # Using full language name
},
{
"text": "Machine learning models require large datasets",
"language": "en", # Using our defined alias
},
# Chinese documents
{
"text": "人工智能正在改变技术领域",
"language": "chinese", # Using full language name
},
{
"text": "机器学习模型需要大型数据集",
"language": "cn", # Using our defined alias
},
]
# Insert the documents
result = client.insert(COLLECTION_NAME, documents)
# Print results
inserted = result["insert_count"]
print(f"Successfully inserted {inserted} documents")
print("Documents by language: 2 English, 2 Chinese")
# Expected output:
# Successfully inserted 4 documents
# Documents by language: 2 English, 2 Chinese
List<String> texts = Arrays.asList(
"Artificial intelligence is transforming technology",
"Machine learning models require large datasets",
"人工智能正在改变技术领域",
"机器学习模型需要大型数据集"
);
List<String> languages = Arrays.asList(
"english", "en", "chinese", "cn"
);
List<JsonObject> rows = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < texts.size(); i++) {
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
row.addProperty("text", texts.get(i));
row.addProperty("language", languages.get(i));
rows.add(row);
}
client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName("multilingual_documents")
.data(rows)
.build());
// Prepare multilingual documents
const documents = [
// English documents
{
text: "Artificial intelligence is transforming technology",
language: "english",
},
{
text: "Machine learning models require large datasets",
language: "en",
},
// Chinese documents
{
text: "人工智能正在改变技术领域",
language: "chinese",
},
{
text: "机器学习模型需要大型数据集",
language: "cn",
},
];
// Insert the documents
const result = await client.insert({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
data: documents,
});
// Print results
const inserted = result.insert_count;
console.log(`Successfully inserted ${inserted} documents`);
console.log("Documents by language: 2 English, 2 Chinese");
// Expected output:
// Successfully inserted 4 documents
// Documents by language: 2 English, 2 Chinese
column1 := column.NewColumnVarChar("text",
[]string{
"Artificial intelligence is transforming technology",
"Machine learning models require large datasets",
"人工智能正在改变技术领域",
"机器学习模型需要大型数据集",
})
column2 := column.NewColumnVarChar("language",
[]string{"english", "en", "chinese", "cn"})
_, err = client.Insert(ctx, milvusclient.NewColumnBasedInsertOption("multilingual_documents").
WithColumns(column1, column2),
)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle err
}
# restful
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{
"collectionName": "multilingual_documents",
"data": [
{
"text": "Artificial intelligence is transforming technology",
"language": "english"
},
{
"text": "Machine learning models require large datasets",
"language": "en"
},
{
"text": "人工智能正在改变技术领域",
"language": "chinese"
},
{
"text": "机器学习模型需要大型数据集",
"language": "cn"
}
]
}'
During insertion, Zilliz Cloud:
-
Reads each document's
languagefield -
Applies the corresponding analyzer to the
textfield -
Generates a sparse vector representation via the BM25 function
-
Stores both the original text and the generated sparse vector
You don't need to provide the sparse vector directly; the BM25 function generates it automatically based on your text and the specified analyzer.
Step 4: Perform search operations
Use English analyzer
When searching with multi-language analyzers, search_params contains crucial configuration:
-
metric_type="BM25"must match your index configuration. -
analyzer_name="english"specifies which analyzer to apply to your query text. This is independent of the analyzers used on stored documents. -
params={"drop_ratio_search": "0"}controls BM25-specific behavior; here, it retains all terms in the search. For more information, refer to Sparse Vector.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
search_params = {
"metric_type": "BM25", # Must match index configuration
"analyzer_name": "english", # Analyzer that matches the query language
"drop_ratio_search": "0", # Keep all terms in search (tweak as needed)
}
# Execute the search
english_results = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME, # Collection to search
data=["artificial intelligence"], # Query text
anns_field="sparse", # Field to search against
search_params=search_params, # Search configuration
limit=3, # Max results to return
output_fields=["text", "language"], # Fields to include in the output
consistency_level="Bounded", # Data‑consistency guarantee
)
# Display English search results
print("\n=== English Search Results ===")
for i, hit in enumerate(english_results[0]):
print(f"{i+1}. [{hit.score:.4f}] {hit.entity.get('text')} "
f"(Language: {hit.entity.get('language')})")
# Expected output (English Search Results):
# 1. [2.7881] Artificial intelligence is transforming technology (Language: english)
Map<String,Object> searchParams = new HashMap<>();
searchParams.put("metric_type", "BM25");
searchParams.put("analyzer_name", "english");
searchParams.put("drop_ratio_search", 0);
SearchResp searchResp = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("multilingual_documents")
.data(Collections.singletonList(new EmbeddedText("artificial intelligence")))
.annsField("sparse")
.topK(3)
.searchParams(searchParams)
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("text", "language"))
.build());
System.out.println("\n=== English Search Results ===");
List<List<SearchResp.SearchResult>> searchResults = searchResp.getSearchResults();
for (List<SearchResp.SearchResult> results : searchResults) {
for (SearchResp.SearchResult result : results) {
System.out.printf("Score: %f, %s\n", result.getScore(), result.getEntity().toString());
}
}
// Execute the search
const english_results = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
data: ["artificial intelligence"],
anns_field: "sparse",
params: {
metric_type: "BM25",
analyzer_name: "english",
drop_ratio_search: "0",
},
limit: 3,
output_fields: ["text", "language"],
consistency_level: "Bounded",
});
// Display English search results
console.log("\n=== English Search Results ===");
english_results.results.forEach((hit, i) => {
console.log(
`${i + 1}. [${hit.score.toFixed(4)}] ${hit.entity.text} ` +
`(Language: ${hit.entity.language})`
);
});
annSearchParams := index.NewCustomAnnParam()
annSearchParams.WithExtraParam("metric_type", "BM25")
annSearchParams.WithExtraParam("analyzer_name", "english")
annSearchParams.WithExtraParam("drop_ratio_search", 0)
resultSets, err := client.Search(ctx, milvusclient.NewSearchOption(
"multilingual_documents", // collectionName
3, // limit
[]entity.Vector{entity.Text("artificial intelligence")},
).WithANNSField("sparse").
WithAnnParam(annSearchParams).
WithOutputFields("text", "language"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
for _, resultSet := range resultSets {
for i := 0; i < len(resultSet.Scores); i++ {
text, _ := resultSet.GetColumn("text").GetAsString(i)
lang, _ := resultSet.GetColumn("language").GetAsString(i)
fmt.Println("Score: ", resultSet.Scores[i], "Text: ", text, "Language:", lang)
}
}
# restful
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{
"collectionName": "multilingual_documents",
"data": ["artificial intelligence"],
"annsField": "sparse",
"limit": 3,
"searchParams": {
"metric_type": "BM25",
"analyzer_name": "english",
"drop_ratio_search": "0"
},
"outputFields": ["text", "language"],
"consistencyLevel": "Strong"
}'
Use Chinese analyzer
This example demonstrates switching to the Chinese analyzer (using its alias "cn") for different query text. All other parameters remain the same, but now the query text is processed using Chinese-specific tokenization rules.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
search_params["analyzer_name"] = "cn"
chinese_results = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME, # Collection to search
data=["人工智能"], # Query text
anns_field="sparse", # Field to search against
search_params=search_params, # Search configuration
limit=3, # Max results to return
output_fields=["text", "language"], # Fields to include in the output
consistency_level="Bounded", # Data‑consistency guarantee
)
# Display Chinese search results
print("\n=== Chinese Search Results ===")
for i, hit in enumerate(chinese_results[0]):
print(f"{i+1}. [{hit.score:.4f}] {hit.entity.get('text')} "
f"(Language: {hit.entity.get('language')})")
# Expected output (Chinese Search Results):
# 1. [3.3814] 人工智能正在改变技术领域 (Language: chinese)
searchParams.put("analyzer_name", "cn");
searchResp = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("multilingual_documents")
.data(Collections.singletonList(new EmbeddedText("人工智能")))
.annsField("sparse")
.topK(3)
.searchParams(searchParams)
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("text", "language"))
.build());
System.out.println("\n=== Chinese Search Results ===");
searchResults = searchResp.getSearchResults();
for (List<SearchResp.SearchResult> results : searchResults) {
for (SearchResp.SearchResult result : results) {
System.out.printf("Score: %f, %s\n", result.getScore(), result.getEntity().toString());
}
}
// Execute the search
const cn_results = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
data: ["人工智能"],
anns_field: "sparse",
params: {
metric_type: "BM25",
analyzer_name: "cn",
drop_ratio_search: "0",
},
limit: 3,
output_fields: ["text", "language"],
consistency_level: "Bounded",
});
// Display Chinese search results
console.log("\n=== Chinese Search Results ===");
cn_results.results.forEach((hit, i) => {
console.log(
`${i + 1}. [${hit.score.toFixed(4)}] ${hit.entity.text} ` +
`(Language: ${hit.entity.language})`
);
});
annSearchParams.WithExtraParam("analyzer_name", "cn")
resultSets, err = client.Search(ctx, milvusclient.NewSearchOption(
"multilingual_documents", // collectionName
3, // limit
[]entity.Vector{entity.Text("人工智能")},
).WithANNSField("sparse").
WithAnnParam(annSearchParams).
WithOutputFields("text", "language"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
for _, resultSet := range resultSets {
for i := 0; i < len(resultSet.Scores); i++ {
text, _ := resultSet.GetColumn("text").GetAsString(i)
lang, _ := resultSet.GetColumn("language").GetAsString(i)
fmt.Println("Score: ", resultSet.Scores[i], "Text: ", text, "Language:", lang)
}
}
# restful
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{
"collectionName": "multilingual_documents",
"data": ["人工智能"],
"annsField": "sparse",
"limit": 3,
"searchParams": {
"analyzer_name": "cn"
},
"outputFields": ["text", "language"],
"consistencyLevel": "Strong"
}'