アナライザの概要
テキスト処理において、アナライザーは生のテキストを構造化された検索可能な形式に変換する重要なコンポーネントです。各アナライザーは通常、トークナイザーとフィルターの2つのコア要素で構成されています。これらを組み合わせることで、入力テキストをトークンに変換し、これらのトークンを改良し、効率的なインデックス作成と検索に備えます。
Zilliz Cloudでは、コレクションスキーマにVARCHARフィールドを追加すると、コレクション作成時にアナライザが設定されます。アナライザによって生成されたトークンは、キーワードマッチングのインデックスを構築したり、全文検索のスパース埋め込みに変換したりするために使用できます。詳細については、「テキスト一致」または「フルテキスト検索」を参照してください。
アナライザーの使用はパフォーマンスに影響を与える可能性があります。
全文検索:全文検索の場合、DataNodeとQuery Nodeチャンネルはトークン化が完了するのを待たなければならないため、データの消費が遅くなります。その結果、新しく取り込まれたデータが検索可能になるまでに時間がかかります。
キーワード一致:キーワード一致の場合、インデックスを作成する前にトークン化が完了する必要があるため、インデックスの作成も遅くなります。
アナライザーの解剖学
Zilliz Cloudのアナライザは、1つのトークナイザとゼロ以上のフィルタで構成されています。
-
トークナイザー:トークナイザーは、入力テキストをトークンと呼ばれる離散的な単位に分割します。これらのトークンは、トークナイザーのタイプに応じて単語やフレーズになる可能性があります。
-
フィルター:フィルターをトークンに適用して、小文字にしたり、一般的な単語を削除したりすることで、トークンをさらに洗練させることができます。
トークナイザーはUTF-8形式のみをサポートしています。他の形式のサポートは将来のリリースで追加されます。
以下のワークフローは、アナライザーがテキストを処理する方法を示しています。
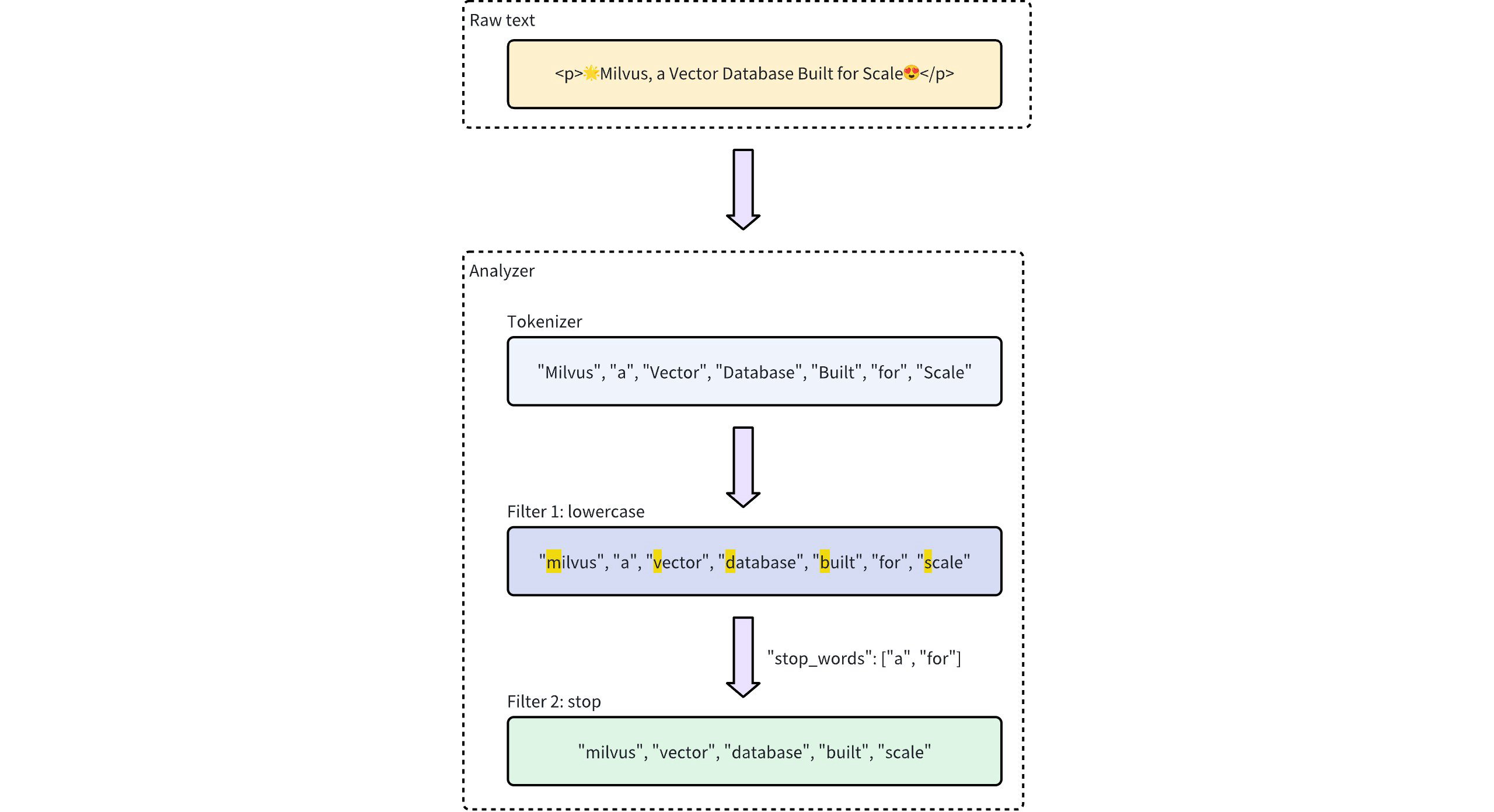
アナライザーの種類
Zilliz Cloudは、異なるテキスト処理ニーズに対応する2種類のアナライザを提供します。
-
組み込みアナライザ:これらは最小限のセットアップで一般的なテキスト処理タスクをカバーする事前定義された構成です。組み込みアナライザは複雑な構成を必要としないため、汎用検索に最適です。
-
カスタムアナライザー:より高度な要件に対して、カスタムアナライザーを使用すると、トークナイザーとゼロ以上のフィルターの両方を指定して独自の構成を定義できます。このカスタマイズレベルは、テキスト処理に対する正確な制御が必要な特殊なユースケースに特に役立ちます。
コレクション作成時にアナライザの設定を省略した場合、Zilliz Cloudはデフォルトですべてのテキスト処理に標準アナライザを使用します。詳細はStandardを参照してください。
内蔵アナライザ
組み込みアナライザZilliz Cloudクラスタには、特定のトークナイザとフィルタが事前に設定されているため、これらのコンポーネントを自分で定義する必要なく、すぐに使用できます。各組み込みアナライザは、カスタマイズのためのオプションパラメータを備えたプリセットトークナイザとフィルタを含むテンプレートとして機能します。
たとえば、標準の組み込みアナライザを使用するには、単純にその名前をstandardとして型として指定し、オプションでstop_wordsなど、このアナライザ型に固有の追加設定を含めます。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
analyzer_params = {
"type": "standard", # Uses the standard built-in analyzer
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"] # Defines a list of common words (stop words) to exclude from tokenization
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("type", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
const analyzer_params = {
"type": "standard", // Uses the standard built-in analyzer
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"] // Defines a list of common words (stop words) to exclude from tokenization
};
export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}'
上記の標準ビルトインアナライザの設定は、次のパラメータを使用してカスタムアナライザを設定するのと同じです。トークナイザとフィルタオプションは、同様の機能を実現するために明示的に定義されています。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter",
Arrays.asList("lowercase",
new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "stop");
put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
}}));
const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
};
export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
}'
Zilliz Cloudには、特定のテキスト処理ニーズに合わせて設計された以下の組み込みアナライザがあります。
-
standard:一般的なテキスト処理に適しており、標準のトークン化と小文字のフィルタリングを適用します。 -
英語:英語のテキストに最適化され、英語のストップワードをサポートしています。 -
中国語:中国語テキストの処理に特化しており、中国語の言語構造に適応したトークン化も含まれます。
組み込みアナライザのリストとカスタマイズ可能な設定については、Built-in Analyzer Referenceを参照してください。
カスタムアナライザ
より高度なテキスト処理のために、Zilliz Cloudのカスタムアナライザーを使用すると、トークナイザーとフィルターの両方を指定して、カスタマイズされたテキスト処理パイプラインを構築できます。このセットアップは、正確な制御が必要な特殊なユースケースに最適です。
トークナイザー
トークナイザーは、カスタムアナライザーの必須コンポーネントであり、入力テキストを離散的な単位またはトークンに分解してアナライザーパイプラインを開始します。トークナイザーは、トークナイザータイプに応じて、空白や句読点で分割するなどの特定のルールに従います。この過程により、各単語やフレーズのより正確で独立した処理が可能になります。
例えば、トークナイザーは「Vector Database Built for Scale」というテキストを別々のトークンに変換します
["Vector", "Database", "Built", "for", "Scale"]
トークナイザーの指定例:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
}
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "whitespace");
const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
};
export analyzerParams='{
"type": "whitespace"
}'
選択できるトークナイザーのリストについては、トークナイザーリファレンスを参照しTokenizer Referenceい。
フィルター
フィルターは、トークナイザーによって生成されたトークンに作用するオプションのコンポーネントであり、必要に応じて変換または改良します。たとえば、トークン化された用語に小文字のフィルターを適用した後["Vector","Database","Built","for","Scale"]、結果は次のようになります:
["vector", "database", "built", "for", "scale"]
カスタムアナライザのフィルタは、設定のニーズに応じて、組み込みまたはカスタムのいずれかにすることができます。
-
組み込みフィルタ: Pre-configuration byZilliz Cloud,最小限の設定が必要です。これらのフィルタは、名前を指定することでそのまま使用できます。以下のフィルタは、直接使用するために組み込まれています:
-
小文字:テキストを小文字に変換し、大文字小文字を区別しないマッチングを保証します。詳細については、Lowercaseを参照してください。 -
ASCII折りたたみ:非ASCII文字をASCII文字に変換し、多言語テキストの処理を簡素化します。詳細については、ASCII foldingを参照してください。 -
アルファヌモンリー:他の文字を削除して英数字のみを保持します。詳細については、アルファヌモンリーを参照してAlphanumonlyい。 -
cnalphanumonly:漢字、英字、数字以外の文字を含むトークンを削除します。詳細については、Cnalphanumonlyを参照してCnalphanumonlyい。 -
cncharonly:中国語以外の文字を含むトークンを削除します。詳細については、Cncharonlyを参照してCncharonlyい。
組み込みフィルタの使用例:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", # Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": ["lowercase"], # Optional: Built-in filter that converts text to lowercase
}Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter", Collections.singletonList("lowercase"));const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", // Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": ["lowercase"], // Optional: Built-in filter that converts text to lowercase
}export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
}' -
-
カスタムフィルタ:カスタムフィルタを使用すると、特殊な設定が可能です。有効なフィルタタイプ(filter. type)を選択し、各フィルタタイプに特定の設定を追加することで、カスタム
フィルタを定義できます。カスタマイズをサポートするフィルタタイプの例:-
stop:ストップワードのリストを設定することで、指定した一般的な単語を削除します(例:"stop_words":["of","to"])。詳細はStopを参照してください。 -
長さ:最大トークン長の設定など、長さの基準に基づいてトークンを除外します。詳細については、Lengthを参照してください。 -
stemmer:より柔軟なマッチングのために、単語をルート形式に縮小します。詳細については、Stemmerを参照してください。
カスタムフィルタの設定例:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", # Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": [
{
"type": "stop", # Specifies 'stop' as the filter type
"stop_words": ["of", "to"], # Customizes stop words for this filter type
}
]
}Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter",
Collections.singletonList(new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "stop");
put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
}}));const analyzer_params = {
"tokenizer": "standard", // Mandatory: Specifies tokenizer
"filter": [
{
"type": "stop", // Specifies 'stop' as the filter type
"stop_words": ["of", "to"], // Customizes stop words for this filter type
}
]
};export analyzerParams='{
"type": "standard",
"filter": [
{
"type": "stop",
"stop_words": ["a", "an", "for"]
}
]
}'使用できるフィルターの種類とその特定のパラメーターについては、Filter Referenceを参照してください。
-
使用例の例
この例では、埋め込み用のベクトルフィールドとテキスト処理機能用の2つのVARCHARフィールドを持つコレクションスキーマを定義しています。各VARCHARフィールドは、異なる処理ニーズを処理するために独自のアナライザ設定で構成されています。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
# Set up a Milvus client
client = MilvusClient(
uri="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
)
# Create schema
schema = client.create_schema(auto_id=True, enable_dynamic_field=False)
# Add fields to schema
# Use a built-in analyzer
analyzer_params_built_in = {
"type": "english"
}
# Add VARCHAR field `title_en`
schema.add_field(
field_name='title_en',
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length=1000,
enable_analyzer=True,
analyzer_params=analyzer_params_built_in,
enable_match=True,
)
# Configure a custom analyzer
analyzer_params_custom = {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase", # Built-in filter
{
"type": "length", # Custom filter
"max": 40
},
{
"type": "stop", # Custom filter
"stop_words": ["of", "to"]
}
]
}
# Add VARCHAR field `title`
schema.add_field(
field_name='title',
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length=1000,
enable_analyzer=True,
analyzer_params=analyzer_params_custom,
enable_match=True,
)
# Add vector field
schema.add_field(field_name="embedding", datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=3)
# Add primary field
schema.add_field(field_name="id", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True)
# Set up index params for vector field
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(field_name="embedding", metric_type="COSINE", index_type="AUTOINDEX")
# Create collection with defined schema
client.create_collection(
collection_name="YOUR_COLLECTION_NAME",
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
// Set up a Milvus client
ConnectConfig config = ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build();
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(config);
// Create schema
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema.builder()
.enableDynamicField(false)
.build();
// Add fields to schema
// Use a built-in analyzer
Map<String, Object> analyzerParamsBuiltin = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParamsBuiltin.put("type", "english");
// Add VARCHAR field `title_en`
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("title_en")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(1000)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.analyzerParams(analyzerParamsBuiltin)
.enableMatch(true)
.build());
// Configure a custom analyzer
Map<String, Object> analyzerParams = new HashMap<>();
analyzerParams.put("tokenizer", "standard");
analyzerParams.put("filter",
Arrays.asList("lowercase",
new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "length");
put("max", 40);
}},
new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("type", "stop");
put("stop_words", Arrays.asList("a", "an", "for"));
}}
)
);
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("title")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(1000)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.analyzerParams(analyzerParams)
.enableMatch(true) // must enable this if you use TextMatch
.build());
// Add vector field
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("embedding")
.dataType(DataType.FloatVector)
.dimension(3)
.build());
// Add primary field
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("id")
.dataType(DataType.Int64)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.build());
// Set up index params for vector field
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("embedding")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.COSINE)
.build());
// Create collection with defined schema
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("YOUR_COLLECTION_NAME")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
import { MilvusClient, DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
// Set up a Milvus client
const client = new MilvusClient("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT");
// Use a built-in analyzer for VARCHAR field `title_en`
const analyzerParamsBuiltIn = {
type: "english",
};
// Configure a custom analyzer for VARCHAR field `title`
const analyzerParamsCustom = {
tokenizer: "standard",
filter: [
"lowercase",
{
type: "length",
max: 40,
},
{
type: "stop",
stop_words: ["of", "to"],
},
],
};
// Create schema
const schema = {
auto_id: true,
fields: [
{
name: "id",
type: DataType.INT64,
is_primary: true,
},
{
name: "title_en",
data_type: DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length: 1000,
enable_analyzer: true,
analyzer_params: analyzerParamsBuiltIn,
enable_match: true,
},
{
name: "title",
data_type: DataType.VARCHAR,
max_length: 1000,
enable_analyzer: true,
analyzer_params: analyzerParamsCustom,
enable_match: true,
},
{
name: "embedding",
data_type: DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR,
dim: 4,
},
],
};
// Set up index params for vector field
const indexParams = [
{
name: "embedding",
metric_type: "COSINE",
index_type: "AUTOINDEX",
},
];
// Create collection with defined schema
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: "YOUR_COLLECTION_NAME",
schema: schema,
index_params: indexParams,
});
console.log("Collection created successfully!");
export schema='{
"autoId": true,
"enabledDynamicField": false,
"fields": [
{
"fieldName": "id",
"dataType": "Int64",
"isPrimary": true
},
{
"fieldName": "title_en",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 1000,
"enable_analyzer": true,
"enable_match": true,
"analyzer_params": {"type": "english"}
}
},
{
"fieldName": "title",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 1000,
"enable_analyzer": true,
"enable_match": true,
"analyzer_params": {
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter":[
"lowercase",
{
"type":"length",
"max":40
},
{
"type":"stop",
"stop_words":["of","to"]
}
]
}
}
},
{
"fieldName": "embedding",
"dataType": "FloatVector",
"elementTypeParams": {
"dim":3
}
}
]
}'
export indexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "embedding",
"metricType": "COSINE",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX"
}
]'
export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
export TOKEN="YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN"
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"YOUR_COLLECTION_NAME\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $indexParams
}"