Merge Data
You can merge data from an existing Zilliz Cloud collection with data from a local file or an external object storage bucket to create a collection that combines data from both sources. This is referred to as a data merging operation, and you can use it as a workaround to add fields with data to an existing collection.
- This feature is currently in PRIVATE PREVIEW. If you are interested in this feature and want to have a try, please do not hesitate to contact Zilliz Cloud support.
Overview
The data merging operation is similar to a LEFT JOIN operation in relational databases, which combines data from a collection and all matching records from the specified data source, storing the merged data in a new collection.
The data source should be a set of PARQUET files stored either in a Zilliz Cloud stage or an object storage bucket.
As shown in the following diagram, there is a collection containing three fields, with the id field serving as the primary key. Additionally, there is a PARQUET file with two fields, named id and date. The id field acts as the merge key, and its value should match those in the source collection. The date field is the field to be added.
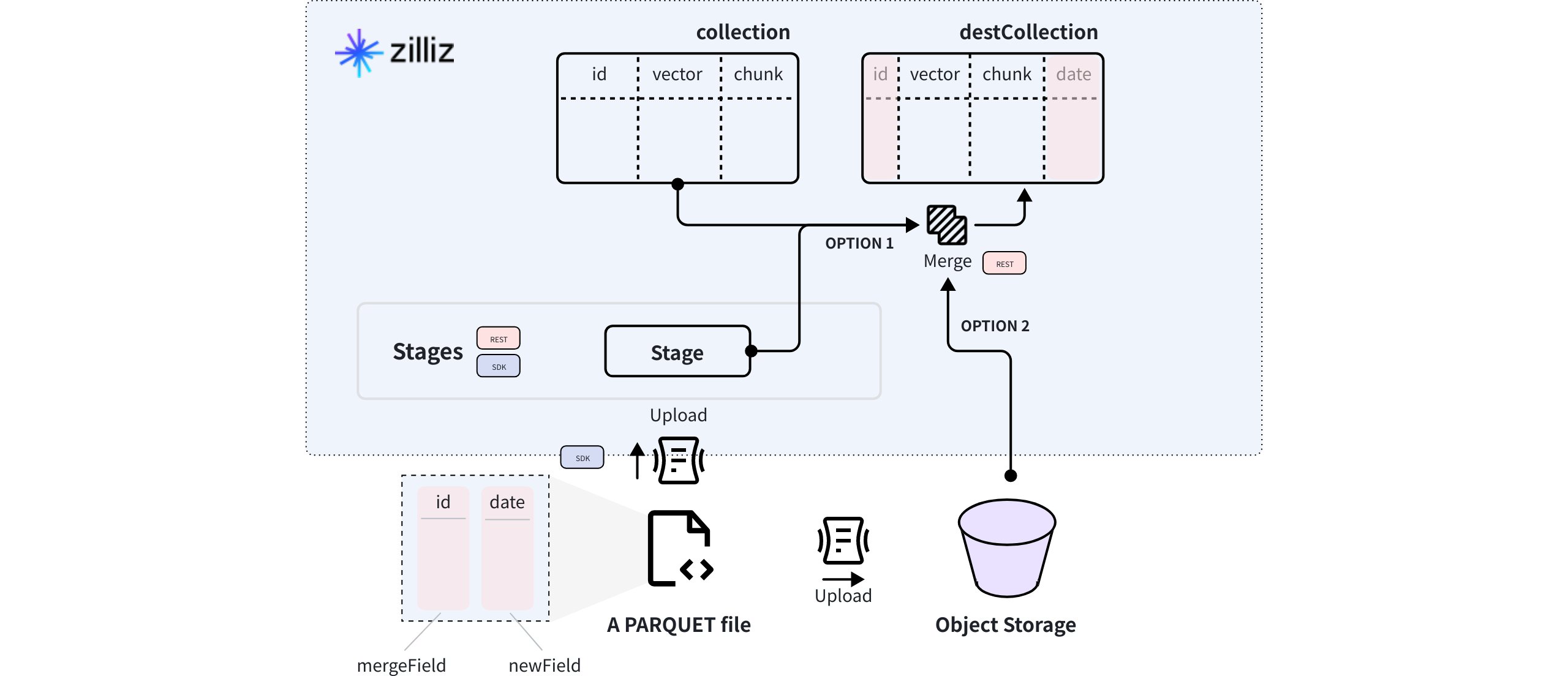
Once you upload the PARQUET file to a Zilliz Cloud stage or an object storage bucket, you can use the Merge Data API to create a target collection that stores data from both sources.
The data source is optional. You can also use the Merge Data API without specifying the data source as a workaround to add fields to an existing collection.
This guide will demonstrate how to use the Merge Data API to add fields with and without data.
Add fields with data
To add fields with data, you need to provide the source collection, the data source, and the new fields to be added to the target collection.
The data source should be a set of PARQUET file either in a Zilliz Cloud stage or an AWS S3 bucket.
Use stage
To perform a data merging operation using a stage, you first create a stage and upload the data from the local file system into it. Once that is done, you can perform a data merge operation to create a new collection that combines the data from both the existing collection and the stage.
The following code snippet demonstrates how to use a stage to perform the data merging operation using a stage. For details on how to create a stage and upload data to it, refer to Manage Stages.
export BASE_URL="https://api.cloud.zilliz.com"
export TOKEN="YOUR_API_KEY"
curl --request POST \
--url "${BASE_URL}/v2/etl/merge" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"clusterId": "in00-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"dbName": "my_database",
"collectionName": "my_collection",
"destDbName": "my_database",
"destCollectionName": "my_merged_collection",
"dataSource": {
"type": "stage",
"stageName": "my_stage",
"dataPath": "path/to/your/parquet.parquet"
},
"mergeField": "id",
"newFields": [
{
"fieldName": "date",
"dataType": "VARCHAR",
"params": {
"maxLength": 10
}
}
]
}'
Before running the above command, there are several fields that you may need to pay attention to:
-
dbNameandcollectionNameThese two parameters determine the source collection of the data merging operation.
-
destDbNameanddestCollectionNameThese two parameters determine the target collection that will be generated after the data merging operation. The target collection should be in the same cluster as the source collection.
-
dataSourceThis parameter is optional and includes the data source settings, such as the data source type and the path to the Parquet file that contains column-wise data, which will be merged with data from the source collection and stored in the target collection.
When using a stage as the intermediate storage spot, you need to set
stageNameanddataPathafter settingtypetostage.📘Notes- The value of the
dataPathparameter can be an absolute path to a file relative to the stage's root, or a folder within the stage that contains multiple Parquet files. If the value points to a folder, ensure that the Parquet files in the folder have the same data structure.
For example, the value could be
path/to/your/file.parquet(file) orpath/to/your/folder/(folder).- You can leave this parameter unspecified if you simply want to add fields without data.
- The value of the
-
mergeFieldThe data merging operation is similar to a LEFT JOIN operation in relational database systems, with the merge field serving as the shared key between the source collection and the Parquet file containing column-wise data.
-
newFieldsThis is a list of schemas for the fields to add to the target collection after the data merging operation. Supported data types are VARCHAR, INT8, INT16, INT32, INT64, FLOAT, DOUBLE, and BOOL.
The above command creates a data merging job and returns its ID.
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"jobId": "job-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
}
}
Use object storage
To perform a data merging operation using an object storage bucket, you first create an object storage bucket and upload the data to it. Once that is done, you can perform a data merge operation to create a new collection that combines the data from both the existing collection and the bucket.
The following code snippet demonstrates how to use an object storage bucket to perform a data merging operation. You can refer to the documents of your block storage service provider to learn how to create a bucket and upload data to it.
export BASE_URL="https://api.cloud.zilliz.com"
export TOKEN="YOUR_API_KEY"
curl --request POST \
--url "${BASE_URL}/v2/etl/merge" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"clusterId": "in00-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"dbName": "my_database",
"collectionName": "my_collection",
"destDbName": "my_database",
"destCollectionName": "my_merged_collection",
"dataSource": {
"type": "s3",
"dataPath": "s3://my_bucket/path/to/your/parquet.parquet",
"credential": {
"accessKey": "xxxx",
"secretKey": "xxxx"
}
},
"mergeField": "id",
"newFields": [
{
"fieldName": "date",
"dataType": "VARCHAR",
"params": {
"maxLength": 10
}
}
]
}'
Before running the above command, there are several fields that you may need to pay attention to:
-
dbNameandcollectionNameThese two parameters determine the source collection of the data merging operation.
-
destDbNameanddestCollectionNameThese two parameters determine the target collection that will be generated after the data merging operation. Note that the target collection should be in the same cluster as the source collection.
-
dataSourceThis parameter is optional and includes the data source settings, such as the data source type and the path to the Parquet file that contains column-wise data, which will be merged with data from the source collection and stored in the target collection.
When using an S3-compatible object storage bucket as the intermediate storage spot, you need to set
dataPathandcredentialafter settingtypetos3.📘Notes- The value of the
dataPathparameter can be an absolute path to a file relative to the bucket's root, or a folder within the bucket that contains multiple Parquet files. If the value points to a folder, ensure that the Parquet files in the folder have the same data structure.
For example, the value could be
s3://path/to/your/file.parquet(file) ors3://path/to/your/folder/(folder).- You can leave this parameter unspecified if you simply want to add fields without data.
- The value of the
-
mergeFieldThe data merging operation is similar to a LEFT JOIN operation in relational database systems, with the merge field serving as the shared key between the source collection and the Parquet file containing column-wise data.
-
newFieldsThis is a list of schemas for the fields to add to the target collection after the data merging operation. Supported data types are VARCHAR, INT8, INT16, INT32, INT64, FLOAT, DOUBLE, and BOOL.
The above command creates a data merging job and returns its ID.
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"jobId": "job-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
}
}
Add fields without data
You can also use the Merge Data API as a workaround to add fields to an existing collection. In this case, you do not need to set the data source.
export BASE_URL="https://api.cloud.zilliz.com"
export TOKEN="YOUR_API_KEY"
curl --request POST \
--url "${BASE_URL}/v2/etl/merge" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"clusterId": "in00-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
"dbName": "my_database",
"collectionName": "my_collection",
"destDbName": "my_database",
"destCollectionName": "my_merged_collection",
"mergeField": "id",
"newFields": [
{
"fieldName": "date",
"dataType": "VARCHAR",
"params": {
"maxLength": 10
}
}
]
}'
The above command creates a data merging job and returns its ID.
{
"code": 0,
"data": {
"jobId": "job-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
}
}
Verify the results
After obtaining the ID of the data merging job, you can use the Describe Job or the steps listed in Manage Project Jobs to check its status in detail.
Once the data merging job is complete, you can check whether the schema of the target collection and the number of entities in the target collection meet your expectations.
Troubleshooting
-
How can I handle the situation where the rows in the Parquet file have merge keys that do not match any entities in the source collection?
Similar to a left join operation in relational database systems, the data merging operation combines all rows from the source collection with matching rows from the specified Parquet file. This results in a new destination collection containing all fields from the source, the fields defined in newFields, and the combined data.
Only rows from the Parquet file with a merge key matching those in the source collection will be merged. Rows are skipped if their merge keys do not match any entity in the source collection. If none of the rows in the Parquet file match any entity, only the fields specified in
newFieldswill be created with null values, if configured.