バイナリベクトル
バイナリベクトルは、従来の高次元浮動小数点ベクトルを0と1のみを含むバイナリベクトルに変換する特別な形式のデータ表現です。この変換により、ベクトルの体格が圧縮されるだけでなく、意味情報を保持しながらストレージおよび計算コストが削減されます。非重要な特徴の精度が必要でない場合、バイナリベクトルは、元の浮動小数点ベクトルのほとんどの整合性と有用性を効果的に維持できます。
バイナリベクトルは、計算効率とストレージ最適化が重要な状況で特に幅広い応用があります。検索エンジンやレコメンデーションシステムなどの大規模なAIシステムでは、大量のデータをリアルタイムで処理することが重要です。バイナリベクトルは、ベクトルの体格を減らすことにより、精度を大幅に犠牲にすることなく、レイテンシと計算コストを低減するのに役立ちます。さらに、バイナリベクトルは、メモリや処理能力が限られているモバイルデバイスや組み込みシステムなどのresource-constrained環境でも役立ちます。バイナリベクトルを使用することで、複雑なAI機能をこれらの制限された設定で実装しながら、高いパフォーマンスを維持することができます。
概要について
バイナリベクトルは、複雑なオブジェクト(画像、テキスト、オーディオなど)を固定長のバイナリ値にエンコードする方法です。Zilliz Cloudクラスターでは、バイナリベクトルは通常、ビット配列またはバイト配列として表されます。たとえば、8次元のバイナリベクトルは[1,0,1,1,0,0,1,0]として表すことができます。
以下の図は、バイナリベクトルがテキストコンテンツ内のキーワードの存在を表す方法を示しています。この例では、10次元のバイナリベクトルを使用して、2つの異なるテキスト(テキスト1とテキスト2)を表します。各次元は語彙内の単語に対応します。1はテキスト内の単語の存在を示し、0はその不在を示します。
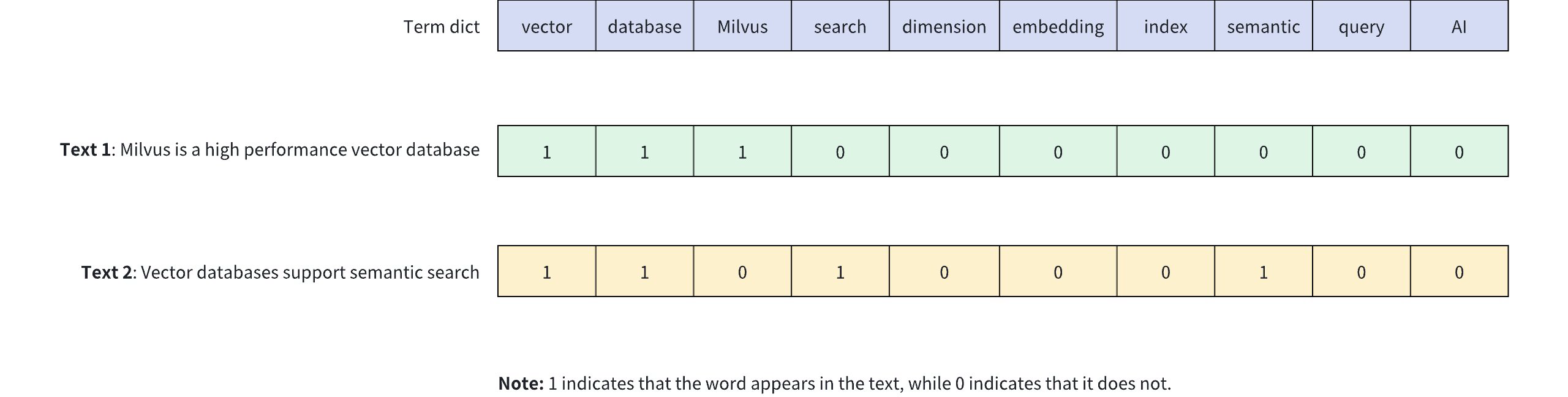
バイナリベクトルには以下の特徴があります。
-
**効率的なストレージ:**各ディメンションは1ビットのストレージのみを必要とし、ストレージスペースを大幅に削減します。
-
**高速計算:**ベクトル間の類似度は、XORなどのビット演算を使用して迅速に計算できます。
-
**固定長:**ベクトルの長さは元のテキストの長さに関係なく一定であり、インデックス作成や検索が容易になります。
-
**シンプルで直感的:**キーワードの存在を直接反映し、特定の特殊な検索タスクに適しています。
バイナリベクトルは、さまざまな方法で生成できます。テキスト処理では、事前に定義された語彙を使用して、単語の存在に基づいて対応するビットを設定できます。画像処理では、知覚ハッシングアルゴリズム(pHashなど)を使用して、画像のバイナリ特徴を生成できます。機械学習アプリケーションでは、モデル出力をバイナリ化してバイナリベクトル表現を取得できます。
バイナリベクトル化後、データは管理とベクトル取得のためにZilliz Cloudクラスターに保存できます。以下の図は基本的な過程を示しています。
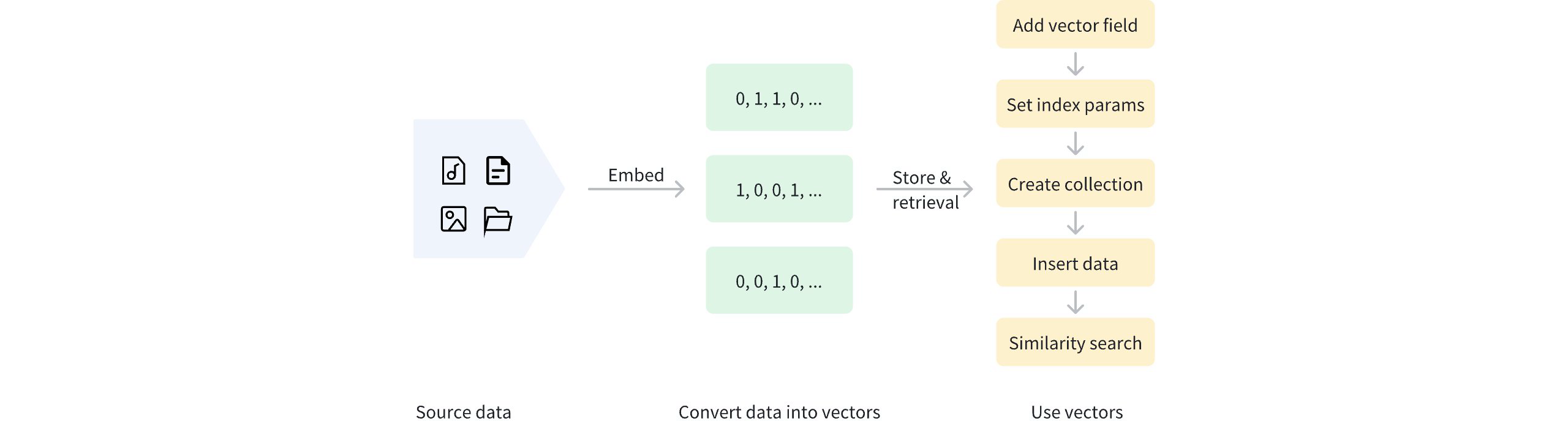
バイナリベクトルを使用
ベクトルフィールドを追加
バイナリベクトルをZilliz Cloudクラスタで使用するには、まずコレクションを作成するときにバイナリベクトルを格納するベクトルフィールドを定義します。この過程には以下が含まれます:
-
datatypeをサポートされているバイナリベクトルデータ型、すなわちBINARY_VECTORに設定します。 -
ベクトルの次元を
dimパラメータを使用して指定します。バイナリベクトルは挿入時にバイト配列に変換する必要があるため、dimは8の倍数でなければなりません。8つのブール値(0または1)ごとに1バイトにパックされます。たとえば、dim=128の場合、挿入には16バイトの配列が必要です。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
client = MilvusClient(uri="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
schema = client.create_schema(
auto_id=True,
enable_dynamic_fields=True,
)
schema.add_field(field_name="pk", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, is_primary=True, max_length=100)
schema.add_field(field_name="binary_vector", datatype=DataType.BINARY_VECTOR, dim=128)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = client.createSchema();
schema.setEnableDynamicField(true);
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("pk")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.maxLength(100)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("binary_vector")
.dataType(DataType.BinaryVector)
.dimension(128)
.build());
import { DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
schema.push({
name: "binary vector",
data_type: DataType.BinaryVector,
dim: 128,
});
export primaryField='{
"fieldName": "pk",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"isPrimary": true,
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 100
}
}'
export vectorField='{
"fieldName": "binary_vector",
"dataType": "BinaryVector",
"elementTypeParams": {
"dim": 128
}
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": true,
\"fields\": [
$primaryField,
$vectorField
],
\"enableDynamicField\": true
}"
この例では、バイナリベクトルを格納するためにbinary_vectorという名前のベクトルフィールドが追加されています。このフィールドのデータ型はBINARY_VECTORで、次元は128です。
ベクトル場のインデックスパラメータを設定する
検索を高速化するために、バイナリベクトル場のインデックスを作成する必要があります。インデックスを作成することで、大規模なベクトルデータの検索効率を大幅に向上させることができます。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="binary_vector",
index_name="binary_vector_index",
index_type="AUTOINDEX",
metric_type="HAMMING"
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import java.util.*;
List<IndexParam> indexParams = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String,Object> extraParams = new HashMap<>();
indexParams.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("binary_vector")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.HAMMING)loca
.build());
import { MetricType, IndexType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const indexParams = {
indexName: "binary_vector_index",
field_name: "binary_vector",
metric_type: MetricType.HAMMING,
index_type: IndexType.AUTOINDEX
};
export indexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "binary_vector",
"metricType": "HAMMING",
"indexName": "binary_vector_index",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX"
}
]'
上記の例では、binary_vector_indexという名前のインデックスがbinary_vectorフィールドに対してAUTOINDEXインデックスタイプを使用して作成されています。メトリックタイプはHAMMINGに設定されており、ハミング距離が類似度測定に使用されていることを示しています。
さらに、Zilliz Cloudはバイナリベクトルに対して他の類似性メトリックをサポートしています。詳細については、「メトリックの種類」を参照してください。
コレクションを作成
バイナリベクトルとインデックスの設定が完了したら、バイナリベクトルを含むコレクションを作成します。以下の例では、create_collectionメソッドを使用してmy_binary_collectionという名前のコレクションを作成します。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
client.create_collection(
collection_name="my_binary_collection",
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_binary_collection")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexParams)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
import { MilvusClient } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const client = new MilvusClient({
address: 'YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT'
});
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: 'my_dense_collection',
schema: schema,
index_params: indexParams
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"my_binary_collection\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $indexParams
}"
データの挿入
コレクションを作成した後、挿入メソッドを使用してバイナリベクトルを含むデータを追加します。バイナリベクトルは、各バイトが8つのブール値を表すバイト配列の形式で提供する必要があることに注意してください。
例えば、128次元のバイナリベクトルの場合、16バイトの配列が必要です(128ビット÷8ビット/バイト=16バイト)。以下はデータを挿入するための例のコードです
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
def convert_bool_list_to_bytes(bool_list):
if len(bool_list) % 8 != 0:
raise ValueError("The length of a boolean list must be a multiple of 8")
byte_array = bytearray(len(bool_list) // 8)
for i, bit in enumerate(bool_list):
if bit == 1:
index = i // 8
shift = i % 8
byte_array[index] |= (1 << shift)
return bytes(byte_array)
bool_vectors = [
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0] + [0] * 112,
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1] + [0] * 112,
]
data = [{"binary_vector": convert_bool_list_to_bytes(bool_vector) for bool_vector in bool_vectors}]
client.insert(
collection_name="my_binary_collection",
data=data
)
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.InsertReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.InsertResp;
private static byte[] convertBoolArrayToBytes(boolean[] booleanArray) {
byte[] byteArray = new byte[booleanArray.length / Byte.SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < booleanArray.length; i++) {
if (booleanArray[i]) {
int index = i / Byte.SIZE;
int shift = i % Byte.SIZE;
byteArray[index] |= (byte) (1 << shift);
}
}
return byteArray;
}
List<JsonObject> rows = new ArrayList<>();
Gson gson = new Gson();
{
boolean[] boolArray = {true, false, false, true, true, false, true, true, false, true, false, false, true, true, false, true};
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
row.add("binary_vector", gson.toJsonTree(convertBoolArrayToBytes(boolArray)));
rows.add(row);
}
{
boolean[] boolArray = {false, true, false, true, false, true, false, false, true, true, false, false, true, true, false, true};
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
row.add("binary_vector", gson.toJsonTree(convertBoolArrayToBytes(boolArray)));
rows.add(row);
}
InsertResp insertR = client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_binary_collection")
.data(rows)
.build());
const data = [
{ binary_vector: [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1] },
{ binary_vector: [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1] },
];
client.insert({
collection_name: "my_binary_collection",
data: data,
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"data\": $data,
\"collectionName\": \"my_binary_collection\"
}"
類似検索を行う
類似検索は、Zilliz Cloudクラスターのコア機能の1つであり、ベクトル間の距離に基づいてクエリベクトルに最も類似したデータをすばやく見つけることができます。バイナリベクトルを使用して類似検索を実行するには、クエリベクトルと検索パラメータを準備し、search()メソッドを呼び出します。
検索操作中には、バイナリベクトルもバイト配列の形式で提供する必要があります。クエリベクトルの次元がdimを定義する際に指定された次元と一致し、8つのブール値が1バイトに変換されるようにしてください。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
search_params = {
"params": {"nprobe": 10}
}
query_bool_list = [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0] + [0] * 112
query_vector = convert_bool_list_to_bytes(query_bool_list)
res = client.search(
collection_name="my_binary_collection",
data=[query_vector],
anns_field="binary_vector",
search_params=search_params,
limit=5,
output_fields=["pk"]
)
print(res)
# Output
# data: ["[{'id': '453718927992172268', 'distance': 10.0, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172268'}}]"]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.BinaryVec;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
Map<String,Object> searchParams = new HashMap<>();
searchParams.put("nprobe",10);
boolean[] boolArray = {true, false, false, true, true, false, true, true, false, true, false, false, true, true, false, true};
BinaryVec queryVector = new BinaryVec(convertBoolArrayToBytes(boolArray));
SearchResp searchR = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_binary_collection")
.data(Collections.singletonList(queryVector))
.annsField("binary_vector")
.searchParams(searchParams)
.topK(5)
.outputFields(Collections.singletonList("pk"))
.build());
System.out.println(searchR.getSearchResults());
// Output
//
// [[SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536775}, score=0.0, id=453444327741536775), SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536776}, score=7.0, id=453444327741536776)]]
query_vector = [1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1];
client.search({
collection_name: 'my_binary_collection',
data: query_vector,
limit: 5,
output_fields: ['pk'],
params: {
nprobe: 10
}
});
export searchParams='{
"params":{"nprobe":10}
}'
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"my_binary_collection\",
\"data\": $data,
\"annsField\": \"binary_vector\",
\"limit\": 5,
\"searchParams\":$searchParams,
\"outputFields\": [\"pk\"]
}"
類似検索パラメータの詳細については、「基本的なベクトル検索」を参照してください。