Phrase Match
Phrase match lets you search for documents containing your query terms as an exact phrase. By default, the words must appear in the same order and directly adjacent to one another. For example, a query for "robotics machine learning" matches text like "…typical robotics machine learning models…", where the words "robotics", "machine", and "learning" appear in sequence with no other words between them.
However, in real-world scenarios, strict phrase matching can be too rigid. You might want to match text like "…machine learning models widely adopted in robotics…". Here, the same keywords are present but not side-by-side or in the original order. To handle this, phrase match supports a slop parameter, which introduces flexibility. The slop value defines how many positional shifts are allowed between the terms in the phrase. For example, with a slop of 1, a query for "machine learning" can match text like "...machine deep learning...", where one word ("deep") separates the original terms.
Overview
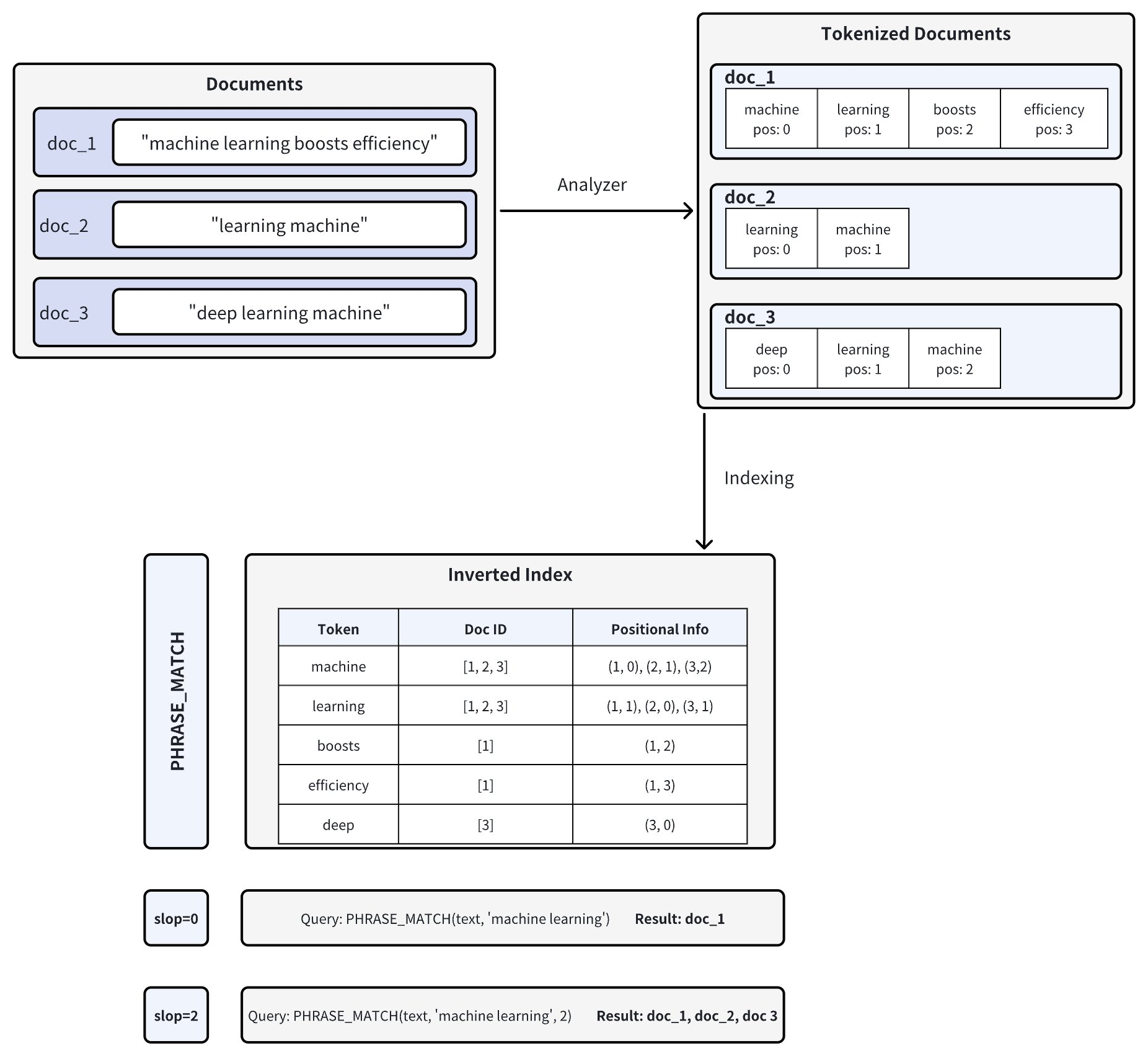
Powered by the Tantivy search engine library, phrase match works by analyzing the positional information of words within documents. The diagram below illustrates the process:
-
Document Tokenization: When you insert documents into Zilliz Cloud, the text is split into tokens (individual words or terms) using an analyzer, with positional information recorded for each token. For example, doc_1 is tokenized into ["machine" (pos=0), "learning" (pos=1), "boosts" (pos=2), "efficiency" (pos=3)]. For more information on analyzers, refer to Analyzer Overview.
-
Inverted Index Creation: Zilliz Cloud builds an inverted index, mapping each token to the document(s) in which it appears and the token's positions in those documents.
-
Phrase Matching: When a phrase query is executed, Zilliz Cloud looks up each token in the inverted index and checks their positions to determine if they appear in the correct order and proximity. The
slopparameter controls the maximum number of positions allowed between matching tokens:-
slop = 0 means the tokens must appear in the exact order and immediately adjacent (i.e., no extra words in between).
- In the example, only doc_1 ("machine" at pos=0, "learning" at pos=1) matches exactly.
-
slop = 2 allows up to two positions of flexibility or rearrangements between matching tokens.
-
This allows reversed order ("learning machine") or a small gap between the tokens.
-
Consequently, doc_1, doc_2 ("learning" at pos=0, "machine" at pos=1), and doc_3 ("learning" at pos=1, "machine" at pos=2) all match.
-
-
Enable phrase match
Phrase match works with the VARCHAR field type, the string data type in Zilliz Cloud.
To enable phrase matching, configure your collection schema by setting both enable_analyzer and enable_match parameters to True. This setup tokenizes your text and builds an inverted index with positional information, enabling efficient phrase searches.
Define schema fields
To enable phrase match for a specific VARCHAR field, set both enable_analyzer and enable_match to True when defining your field schema.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
# Set up a MilvusClient
CLUSTER_ENDPOINT = "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
TOKEN = "YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN"
client = MilvusClient(
uri=CLUSTER_ENDPOINT,
token=TOKEN
)
# Create a schema for a new collection
schema = client.create_schema(enable_dynamic_field=False)
# Add a primary key field
schema.add_field(
field_name="id",
datatype=DataType.INT64,
is_primary=True,
auto_id=True
)
# Add a VARCHAR field configured for phrase matching
schema.add_field(
field_name="text", # Name of the field
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, # Field data type set as VARCHAR (string)
max_length=1000, # Maximum string length
enable_analyzer=True, # Required. Enables text analysis
enable_match=True, # Required. Enables inverted indexing for phrase matching
# Optional: Use a custom analyzer for better phrase matching in specific languages.
# analyzer_params = {"type": "english"} # Example: English analyzer; uncomment to apply custom analyzer
)
# Add a vector field for embeddings
schema.add_field(
field_name="embeddings",
datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR,
dim=5
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.token("YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema.builder()
.build();
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("id")
.dataType(DataType.Int64)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("text")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(1000)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.enableMatch(true)
// Optional: Use a custom analyzer for better phrase matching in specific languages.
// .analyzerParams(Map.of("type", "english")) // Example: English analyzer; uncomment to apply custom analyzer
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("embeddings")
.dataType(DataType.FloatVector)
.dimension(5)
.build());
// Set up a MilvusClient
const address = "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
const token = "YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN"
const client = new MilvusClient({address, token})
const schema = {
collection_name: 'tech_articles',
fields: [
{
name: "id",
description: "primary id",
data_type: DataType.Int64,
is_primary_key: true,
autoID: true,
},
{
name: "text",
description: "text field for phrase matching",
data_type: DataType.VarChar,
max_length: 1000,
enable_analyzer: true, // Enables text analysis
enable_match: true, // Enables inverted indexing for
},
{
name: "embeddings",
description: "vector field",
data_type: DataType.FloatVector,
dim: 5,
},
],
};
import (
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/entity"
)
milvusAddr := "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
APIKey := "YOUR_API_KEY"
client, err := milvusclient.New(ctx, &milvusclient.ClientConfig{
Address: milvusAddr,
APIKey: APIKey
})
schema := entity.NewSchema().WithName(collectionName).
WithField(entity.NewField().WithName("id").WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeInt64).WithIsPrimaryKey(true)).
WithField(entity.NewField().WithName("text").WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).WithMaxLength(1000).WithEnableMatch(true).WithEnableAnalyzer(true)).
WithField(entity.NewField().WithName("embeddings").WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeFloatVector).WithDim(5))
export idField='{
"fieldName": "id",
"dataType": "Int64",
"isPrimary": true,
"autoID": true
}'
export textField='{
"fieldName": "text",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 1000,
"enable_analyzer": true,
"enable_match": true
}
}'
export vectorField='{
"fieldName": "embeddings",
"dataType": "FloatVector",
"elementTypeParams": {
"dim": 5
}
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": false,
\"enableDynamicField\": true,
\"fields\": [
$idField,
$textField,
$vectorField
]
}"
By default, Zilliz Cloud uses the standard analyzer, which tokenizes text by whitespace and punctuation and converts text to lowercase.
If your text data is in a specific language or format, you can configure a custom analyzer using the analyzer_params parameter (for example, { "type": "english" } or { "type": "jieba" }).
See the Analyzer Overview for details.
Create the collection
Oncet the necessary fields are defined, use the following code to create the collection:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Create the collection
COLLECTION_NAME = "tech_articles" # Name your collection
if client.has_collection(COLLECTION_NAME):
client.drop_collection(COLLECTION_NAME)
client.create_collection(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
schema=schema
)
String COLLECTION_NAME = "tech_articles"; // Name your collection
if (client.hasCollection(
HasCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.build()
)) {
client.dropCollection(
DropCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.build()
);
}
client.createCollection(
CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.collectionSchema(schema)
.build()
);
// Create or recreate the collection if it already exists
const COLLECTION_NAME = "tech_articles"; // Name your collection
const hasCollection = await client.hasCollection({ collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME });
if (hasCollection.value) {
await client.dropCollection({ collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME });
}
await client.createCollection(schema);
// go
# restful
# check collection exist
export MILVUS_HOST="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
export COLLECTION_NAME="tech_articles"
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/collections/has" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"$COLLECTION_NAME\"
}"
# drop existing collection
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/collections/drop" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\"
}"
# create new collection
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{
\"collectionName\": \"$COLLECTION_NAME\",
\"schema\": $schema
}"
After the collection is created, make sure the following necessary steps are performed before using pharse match:
-
Entities are inserted into the collection;
-
You have created an index on each vector field;
-
The collection is loaded into memory.
Show example code
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Insert sample data with text containing "machine learning" phrases
sample_data = [
{
"text": "Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.",
"embeddings": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]
},
{
"text": "Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.",
"embeddings": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
},
{
"text": "The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.",
"embeddings": [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7]
},
{
"text": "Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.",
"embeddings": [0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8]
},
{
"text": "This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.",
"embeddings": [0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]
}
]
# Insert the data
client.insert(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
data=sample_data
)
# Index the vector field and load the collection
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="embeddings",
index_type="AUTOINDEX",
index_name="embeddings_index",
metric_type="COSINE"
)
client.create_index(collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME, index_params=index_params)
client.load_collection(collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME)
// Insert sample data with text containing "machine learning" phrases
List<JsonObject> sampleData = Arrays.asList(
createSample("Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.", new float[]{0.1f, 0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f}),
createSample("Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.", new float[]{0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f, 0.6f}),
createSample("The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.", new float[]{0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f, 0.6f, 0.7f}),
createSample("Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.", new float[]{0.4f, 0.5f, 0.6f, 0.7f, 0.8f}),
createSample("This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.", new float[]{0.5f, 0.6f, 0.7f, 0.8f, 0.9f})
);
client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.data(sampleData)
.build());
// Index the vector field and load the collection
IndexParam indexParam = IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("embeddings")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.indexName("embeddings_index")
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.COSINE)
.build();
client.createIndex(CreateIndexReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.indexParams(Collections.singletonList(indexParam))
.build());
client.loadCollection(LoadCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.build());
// Format and insert sample data for "machine learning" phrase matching
const sampleData = [
{
text: "Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.",
embeddings: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
},
{
text: "Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.",
embeddings: [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6],
},
{
text: "The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.",
embeddings: [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7],
},
{
text: "Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.",
embeddings: [0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8],
},
{
text: "This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.",
embeddings: [0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9],
},
];
// Insert the data into the collection
await client.insert({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
data: sampleData,
});
// Create an index on the vector field and load the collection
await client.createIndex({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
field_name: "embeddings",
index_type: "AUTOINDEX",
index_name: "embeddings_index",
metric_type: "COSINE",
});
await client.loadCollection({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
});
// go
# restful
# Insert the data into the collection
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles",
"data": [
{
"text": "Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.",
"embeddings": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]
},
{
"text": "Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.",
"embeddings": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
},
{
"text": "The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.",
"embeddings": [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7]
},
{
"text": "Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.",
"embeddings": [0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8]
},
{
"text": "This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.",
"embeddings": [0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]
}
]
}'
# Create an index on the vector field and load the collection
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/indexes/create" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles",
"indexParams": [
{
"fieldName": "embeddings",
"indexName": "embeddings_index",
"metricType": "COSINE",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX"
}
]
}'
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/collections/load" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles"
}'
Use phrase match
Once you've enabled match for a VARCHAR field in your collection schema, you can perform phrase matches using the PHRASE_MATCH expression.
The PHRASE_MATCH expression is case-insensitive. You can use either PHRASE_MATCH or phrase_match.
PHRASE_MATCH expression syntax
Use the PHRASE_MATCH expression to specify the field, phrase, and optional flexibility (slop) when searching. The syntax is:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)
String filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')";
PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)
// go
# restful
export filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)"
-
field_name: The name of theVARCHARfield on which you perform phrase matches. -
phrase: The exact phrase to search for. -
slop(optional): An integer specifying the maximum number of positions allowed in matching tokens.-
0(default): Matches exact phrases only. Example: A filter for "machine learning" will match "machine learning" exactly, but not "machine boosts learning" or "learning machine". -
1: Allows minor variation, such as one extra term or minor shift in position. Example: A filter for "machine learning" will match "machine boosts learning" (one token between "machine" and "learning") but not "learning machine" (terms reversed). -
2: Allows more flexibility, including reversed term order or up to two tokens in between. Example: A filter for "machine learning" will match "learning machine" (terms reversed) or "machine quickly boosts learning" (two tokens between "machine" and "learning").
-
Query with phrase match
When using the query() method, PHRASE_MATCH acts as a scalar filter. Only documents that contain the specified phrase (subject to the allowed slop) are returned.
Example: slop = 0 (exact match)
This example returns documents containing the exact phrase "machine learning" without any extra tokens in between.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Match documents containing exactly "machine learning"
filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')"
result = client.query(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
filter=filter,
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Query result: ", result)
# Expected output:
# Query result: data: ["{'id': 461366973343948097, 'text': 'Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.'}", "{'id': 461366973343948099, 'text': 'The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.'}", "{'id': 461366973343948100, 'text': 'Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.'}"]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.QueryReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.QueryResp;
String filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')";
QueryResp result = client.query(QueryReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.filter(filter)
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build());
const filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')";
const result = await client.query({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
filter: filter,
output_fields: ["id", "text"]
});
// go
# restful
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/entities/query" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles",
"filter": "PHRASE_MATCH(text, '\''machine learning'\'')",
"outputFields": ["id", "text"],
"limit": 100
}'
Search with phrase match
In search operations, PHRASE_MATCH is used to pre-filter documents before applying vector similarity ranking. This two-step approach first narrows the candidate set by textual matching and then re-ranks those candidates based on vector embeddings.
Example: slop = 1
Here, we allow a slop of 1. The filter is applied to documents that contain the phrase "learning machine" with slight flexibility.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Example: Filter documents containing "learning machine" with slop=1
filter_slop1 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)"
result_slop1 = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field="embeddings",
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
filter=filter_slop1,
search_params={},
limit=10,
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Slop 1 result: ", result_slop1)
# Expected output:
# Slop 1 result: data: [[{'id': 461366973343948098, 'distance': 0.9949367046356201, 'entity': {'text': 'Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.', 'id': 461366973343948098}}, {'id': 461366973343948101, 'distance': 0.9710607528686523, 'entity': {'text': 'This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.', 'id': 461366973343948101}}]]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
String filterSlop1 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)";
List<Float> queryVector = Arrays.asList(0.1f, 0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f);
SearchResp resultSlop1 = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.annsField("embeddings")
.data(Collections.singletonList(queryVector))
.filter(filterSlop1)
.searchParams(Collections.emptyMap())
.topK(10)
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build());
System.out.println("Slop 1 result: " + resultSlop1);
const filter_slop1 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)";
const result_slop1 = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field: "embeddings",
data: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
filter: filter_slop1,
limit: 10,
output_fields: ["id", "text"],
});
// go
# restful
export MILVUS_HOST="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
export COLLECTION_NAME="tech_articles"
export AUTH_TOKEN="your_token_here"
# Search数据
echo "Searching with PHRASE_MATCH filter (slop=1)..."
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${AUTH_TOKEN}" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\",
\"annsField\": \"embeddings\",
\"data\": [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
\"filter\": \"PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)\",
\"searchParams\": {},
\"limit\": 10,
\"outputFields\": [\"id\", \"text\"]
}"
Example: slop = 2
This example allows a slop of 2, meaning that up to two extra tokens (or reversed terms) are allowed between the words "machine" and "learning".
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=2
filter_slop2 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 2)"
result_slop2 = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field="embeddings", # Vector field name
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]], # Query vector
filter=filter_slop2, # Filter expression
search_params={},
limit=10, # Maximum results to return
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Slop 2 result: ", result_slop2)
# Expected output:
# Slop 2 result: data: [[{'id': 461366973343948097, 'distance': 0.9999999403953552, 'entity': {'text': 'Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.', 'id': 461366973343948097}}, {'id': 461366973343948098, 'distance': 0.9949367046356201, 'entity': {'text': 'Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.', 'id': 461366973343948098}}, {'id': 461366973343948099, 'distance': 0.9864400029182434, 'entity': {'text': 'The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.', 'id': 461366973343948099}}, {'id': 461366973343948100, 'distance': 0.9782319068908691, 'entity': {'text': 'Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.', 'id': 461366973343948100}}, {'id': 461366973343948101, 'distance': 0.9710607528686523, 'entity': {'text': 'This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.', 'id': 461366973343948101}}]]
// Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=2
String filterSlop2 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 2)";
SearchReq searchReqSlop2 = SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.annsField("embeddings") // Vector field name
.data(queryVector) // Query vector
.filter(filterSlop2) // Filter expression
.searchParams(new HashMap<>())
.topK(10) // Maximum results to return
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build();
SearchResp resultSlop2 = client.search(searchReqSlop2);
System.out.println("Slop 2 result: " + resultSlop2);
const filter_slop2 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 2)";
const result_slop2 = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field: "embeddings",
data: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
filter: filter_slop2,
limit: 10,
output_fields: ["id", "text"],
});
// go
#restful
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${AUTH_TOKEN}" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\",
\"annsField\": \"embeddings\",
\"data\": [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
\"filter\": \"PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 2)\",
\"searchParams\": {},
\"limit\": 10,
\"outputFields\": [\"id\", \"text\"]
}"
Example: slop = 3
In this example, a slop of 3 provides even more flexibility. The filter searches for "machine learning" with up to three token positions allowed between the words.
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=3
filter_slop3 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 3)"
result_slop3 = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field="embeddings", # Vector field name
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]], # Query vector
filter=filter_slop3, # Filter expression
search_params={},
limit=10, # Maximum results to return
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Slop 3 result: ", result_slop3)
# Expected output:
# Slop 3 result: data: [[{'id': 461366973343948097, 'distance': 0.9999999403953552, 'entity': {'text': 'Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.', 'id': 461366973343948097}}, {'id': 461366973343948098, 'distance': 0.9949367046356201, 'entity': {'text': 'Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.', 'id': 461366973343948098}}, {'id': 461366973343948099, 'distance': 0.9864400029182434, 'entity': {'text': 'The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.', 'id': 461366973343948099}}, {'id': 461366973343948100, 'distance': 0.9782319068908691, 'entity': {'text': 'Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.', 'id': 461366973343948100}}, {'id': 461366973343948101, 'distance': 0.9710607528686523, 'entity': {'text': 'This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.', 'id': 461366973343948101}}]]
// Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=3
String filterSlop3 = String.format("PHRASE_MATCH(text, '%s', %d)", "machine learning", 3);
SearchResp resultSlop3 = client.search(
SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.annsField("embeddings") // Vector field name
.data(queryVector) // Query vector
.filter(filterSlop3) // Filter expression
.searchParams(new HashMap<>())
.topK(10) // Maximum results to return
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build()
);
System.out.printf("Slop 3 result: %s%n", resultSlop3);
const filter_slop3 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 3)";
const result_slop3 = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field: "embeddings",
data: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
filter: filter_slop3,
limit: 10,
output_fields: ["id", "text"],
});
// go
# restful
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${AUTH_TOKEN}" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\",
\"annsField\": \"embeddings\",
\"data\": [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
\"filter\": \"PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 3)\",
\"searchParams\": {},
\"limit\": 10,
\"outputFields\": [\"id\", \"text\"]
}"
Considerations
-
Enabling phrase matching for a field triggers the creation of an inverted index, which consumes storage resources. Consider storage impact when deciding to enable this feature, as it varies based on text size, unique tokens, and the analyzer used.
-
Once you've defined an analyzer in your schema, its settings become permanent for that collection. If you decide that a different analyzer would better suit your needs, you may consider dropping the existing collection and creating a new one with the desired analyzer configuration.
-
Phrase match performance depends on how text is tokenized. Before applying an analyzer to your entire collection, use the
run_analyzermethod to review the tokenization output. For more information, refer to Analyzer Overview. -
Escape rules in
filterexpressions:-
Characters enclosed in double quotes or single quotes within expressions are interpreted as string constants. If the string constant includes escape characters, the escape characters must be represented with escape sequence. For example, use
\\to represent\,\\tto represent a tab\t, and\\nto represent a newline. -
If a string constant is enclosed by single quotes, a single quote within the constant should be represented as
\\'while a double quote can be represented as either"or\\". Example:'It\\'s milvus'. -
If a string constant is enclosed by double quotes, a double quote within the constant should be represented as
\\"while a single quote can be represented as either'or\\'. Example:"He said \\"Hi\\"".
-