密集ベクトル
密集ベクトルは、機械学習やデータ分析で広く使用されている数値データ表現です。実数の配列で構成され、ほとんどまたはすべての要素が非ゼロです。疎ベクトルと比較して、密集ベクトルは、各次元が意味のある値を保持するため、同じ次元レベルでより多くの情報を含んでいます。この表現により、複雑なパターンや関係を効果的に捉えることができ、データを高次元空間で分析および過程化することが容易になります。密集ベクトルには通常、特定のアプリケーションや要件に応じて、数十から数百、さらには数千の固定された次元があります。
密集ベクトルは、セマンティック検索や推薦システムなど、データの意味を理解する必要があるシナリオで主に使用されます。セマンティック検索では、密集ベクトルはクエリとドキュメントの根本的なつながりを捉え、検索結果の関連性を向上させるのに役立ちます。推薦システムでは、ユーザーとアイテムの類似点を特定し、よりパーソナライズされた提案を提供するのに役立ちます。
概要について
密ベクトルは通常、固定長の浮動小数点数の配列として表されます(例:[0.2,0.7,0.1,0.8,0.3,...)。。。0.5]。これらのベクトルの次元数は通常、128、256、768、または1024など、数百から数千に及びます。各次元はオブジェクトの特定の意味的特徴を捉えるため、類似性計算を通じてさまざまなシナリオに適用できます。
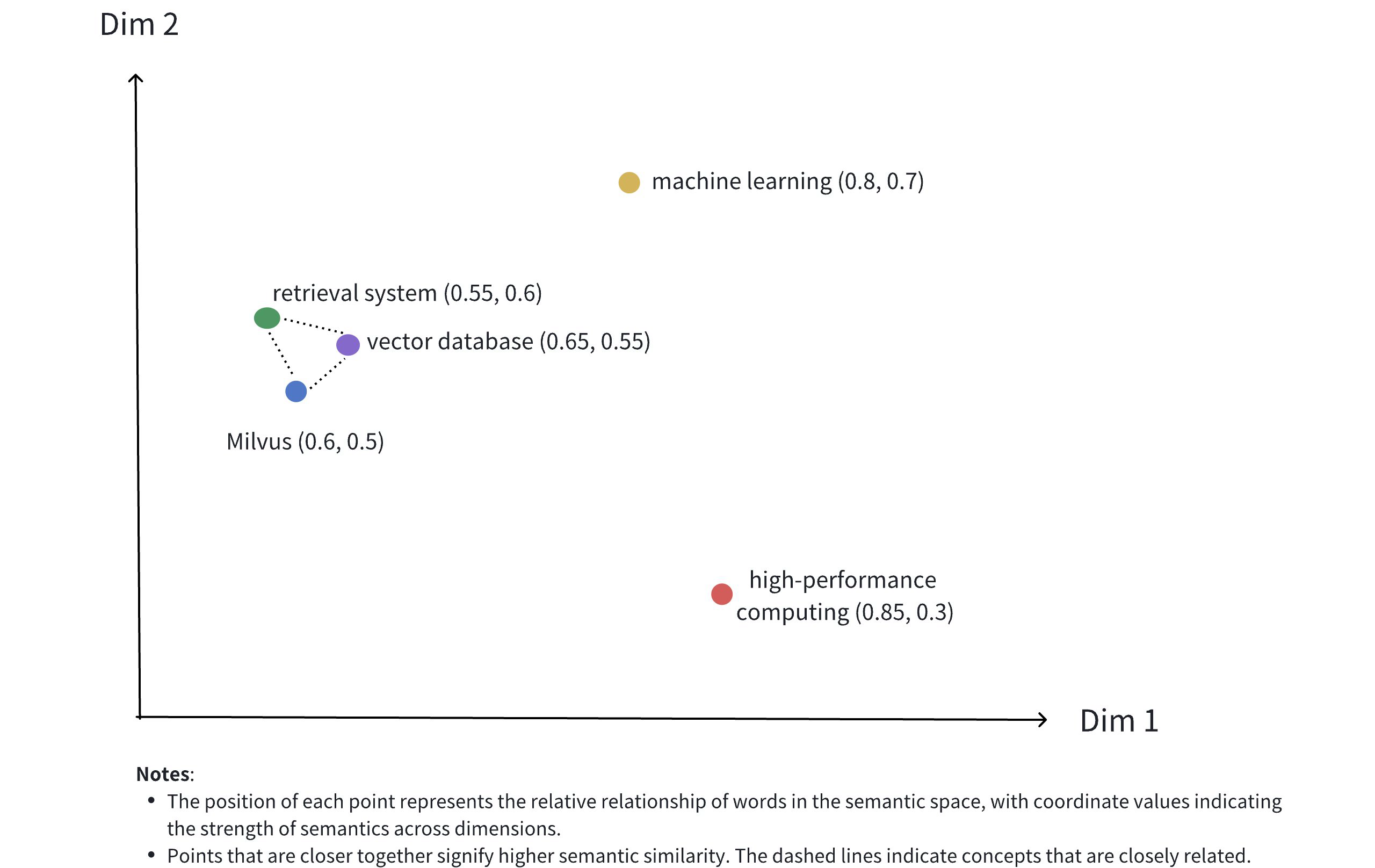
上の画像は、2 D空間における密集ベクトルの表現を示しています。現実世界のアプリケーションにおける密集ベクトルはしばしばはるかに高次元を持っていますが、この2 Dイラストはいくつかの重要な概念を効果的に伝えています
-
**多次元表現:**各点は概念オブジェクト(Milvus、ベクトルデータベース、検索システムなど)を表し、その位置はその次元の値によって決定されます。
-
**意味関係:**ポイント間の距離は、概念間の意味的類似性を反映しています。より近いポイントは、より意味的に関連する概念を示します。
-
**クラスタリング効果:**関連する概念(Milvus、ベクトルデータベース、検索システムなど)は、空間内で互いに近接して配置され、意味的クラスタを形成します。
以下は、「Milvusは効率的なベクトルデータベースである」というテキストを表す実密ベクトルの例です
[
-0.013052909,
0.020387933,
-0.007869,
-0.11111383,
-0.030188112,
-0.0053388323,
0.0010654867,
0.072027855,
// ... more dimensions
]
密ベクトルは、CNNモデル(ResNet、VGGなど)や言語モデル(BERT、Word 2Vecなど)など、さまざまなembeddingモデルを使用して生成できます。これらのモデルは、生データを高次元空間の点に変換し、データの意味的特徴をキャプチャします。さらに、Zilliz Cloudは、Embeddingsで詳しく説明されているように、過程的で密なベクトルを生成するための便利な方法を提供しています。
データがベクトル化されると、管理とベクトル取得のためにZilliz Cloudクラスターに保存できます。以下の図は基本的な過程を示しています。
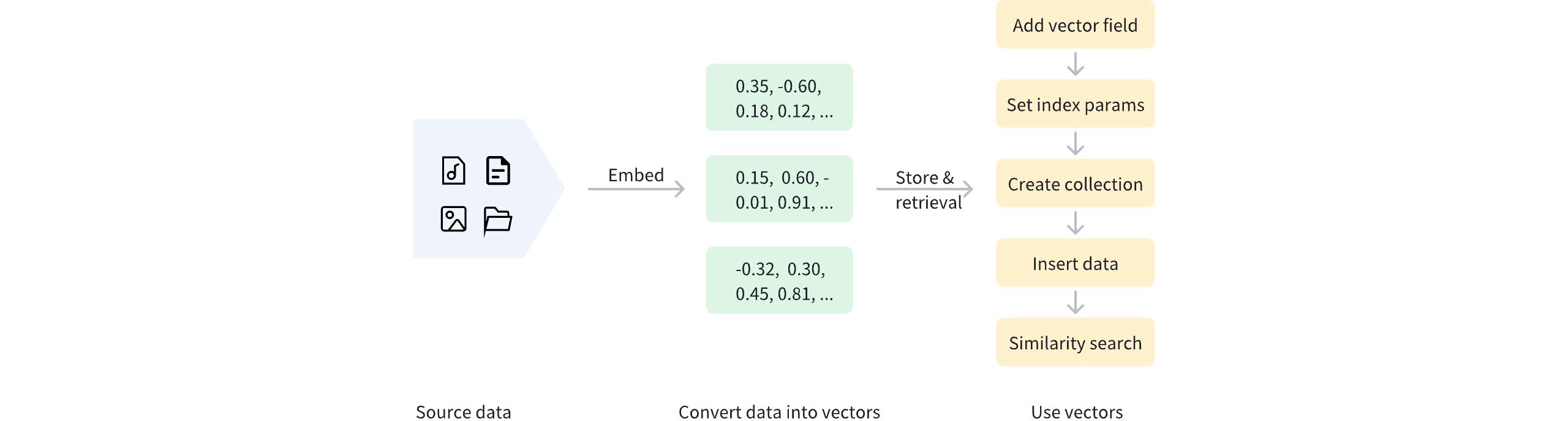
高密度ベクトルを使用する
ベクトルフィールドを追加
コレクションを作成する際に、Zilliz Cloudクラスターで密集ベクトルを使用するには、まず密集ベクトルを格納するベクトルフィールドを定義します。この過程には以下が含まれます:
-
サポートされている高密度ベクトルデータ型に
datatypeを設定します。サポートされている高密度ベクトルデータ型については、データ型を参照してください。 -
密ベクトルの次元を
dimパラメータを使用して指定します。
以下の例では、高密度ベクトルを格納するためにdense_vectorという名前のベクトルフィールドを追加します。フィールドのデータ型はFLOAT_VECTORで、次元は4です。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
client = MilvusClient(uri="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
schema = client.create_schema(
auto_id=True,
enable_dynamic_fields=True,
)
schema.add_field(field_name="pk", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, is_primary=True, max_length=100)
schema.add_field(field_name="dense_vector", datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=4)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = client.createSchema();
schema.setEnableDynamicField(true);
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("pk")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.maxLength(100)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("dense_vector")
.dataType(DataType.FloatVector)
.dimension(4)
.build());
import { DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
schema.push({
name: "dense_vector",
data_type: DataType.FloatVector,
dim: 128,
});
export primaryField='{
"fieldName": "pk",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"isPrimary": true,
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 100
}
}'
export vectorField='{
"fieldName": "dense_vector",
"dataType": "FloatVector",
"elementTypeParams": {
"dim": 4
}
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": true,
\"fields\": [
$primaryField,
$vectorField
]
}"
高密度ベクトルフィールドでサポートされるデータ型:
データ型 | 説明する |
|---|---|
| 32ビット浮動小数点数を格納し、科学計算や機械学習で実数を表現するために一般的に使用されます。類似するベクトルを区別するなど、高精度が必要なシナリオに最適です。 |
| 16ビットの半精度浮動小数点数を格納し、深層学習やGPU計算に使用されます。精度が重要でないシナリオ、例えばレコメンデーションシステムの低精度リコールフェーズでストレージスペースを節約します。 |
| 16ビットのBrain Floating Point(bfloat16)数値を格納し、Float 32と同じ範囲の指数を提供しますが、精度が低下します。大規模な画像取得など、大量のベクトルを迅速に処理する必要があるシナリオに適しています。 |
ベクトル場のインデックスパラメータを設定する
意味検索を加速するためには、ベクトル場のインデックスを作成する必要があります。インデックス化は、大規模なベクトルデータの検索効率を大幅に向上させることができます。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="dense_vector",
index_name="dense_vector_index",
index_type="AUTOINDEX",
metric_type="IP"
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import java.util.*;
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("dense_vector")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.IP)
.build());
import { MetricType, IndexType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const indexParams = {
index_name: 'dense_vector_index',
field_name: 'dense_vector',
metric_type: MetricType.IP,
index_type: IndexType.AUTOINDEX
};
export indexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "dense_vector",
"metricType": "IP",
"indexName": "dense_vector_index",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX"
}
]'
上記の例では、dence_vector_indexという名前のインデックスが、dence_vectorフィールドに対してAUTOINDEXインデックスタイプを使用して作成されます。メトリックタイプはIPに設定されており、内積が距離メトリックとして使用されることを示しています。
Zilliz Cloudは他のメトリックタイプをサポートしています。詳細については、「メトリックの種類」を参照してください。
コレクションを作成
密ベクトルとインデックスパラメータの設定が完了したら、密ベクトルを含むコレクションを作成できます。以下の例では、create_collectionメソッドを使用して、my_dence_collectionという名前のコレクションを作成しています。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
client.create_collection(
collection_name="my_dense_collection",
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_dense_collection")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
import { MilvusClient } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const client = new MilvusClient({
address: 'YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT'
});
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: 'my_dense_collection',
schema: schema,
index_params: indexParams
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"my_dense_collection\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $indexParams
}"
データの挿入
コレクションを作成した後、挿入メソッドを使用して、高密度ベクトルを含むデータを追加します。挿入される高密度ベクトルの次元が、高密度ベクトルフィールドを追加するときに定義されたdim値と一致することを確認してください。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
data = [
{"dense_vector": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.7]},
{"dense_vector": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.8]},
]
client.insert(
collection_name="my_dense_collection",
data=data
)
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.InsertReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.InsertResp;
List<JsonObject> rows = new ArrayList<>();
Gson gson = new Gson();
rows.add(gson.fromJson("{\"dense_vector\": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]}", JsonObject.class));
rows.add(gson.fromJson("{\"dense_vector\": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]}", JsonObject.class));
InsertResp insertR = client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_dense_collection")
.data(rows)
.build());
const data = [
{ dense_vector: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.7] },
{ dense_vector: [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.8] },
];
client.insert({
collection_name: "my_dense_collection",
data: data,
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"data": [
{"dense_vector": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]},
{"dense_vector": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]}
],
"collectionName": "my_dense_collection"
}'
## {"code":0,"cost":0,"data":{"insertCount":2,"insertIds":["453577185629572531","453577185629572532"]}}
類似検索を行う
密集ベクトルに基づく意味検索は、Zilliz Cloudクラスターのコア機能の1つであり、ベクトル間の距離に基づいてクエリベクトルに最も類似したデータをすばやく見つけることができます。類似検索を実行するには、クエリベクトルと検索パラメータを準備し、検索メソッドを呼び出します。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
search_params = {
"params": {"nprobe": 10}
}
query_vector = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.7]
res = client.search(
collection_name="my_dense_collection",
data=[query_vector],
anns_field="dense_vector",
search_params=search_params,
limit=5,
output_fields=["pk"]
)
print(res)
# Output
# data: ["[{'id': '453718927992172271', 'distance': 0.7599999904632568, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172271'}}, {'id': '453718927992172270', 'distance': 0.6299999952316284, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172270'}}]"]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.FloatVec;
Map<String,Object> searchParams = new HashMap<>();
searchParams.put("nprobe",10);
FloatVec queryVector = new FloatVec(new float[]{0.1f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 0.4f});
SearchResp searchR = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_dense_collection")
.data(Collections.singletonList(queryVector))
.annsField("dense_vector")
.searchParams(searchParams)
.topK(5)
.outputFields(Collections.singletonList("pk"))
.build());
System.out.println(searchR.getSearchResults());
// Output
//
// [[SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536779}, score=0.65, id=453444327741536779), SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536778}, score=0.65, id=453444327741536778)]]
query_vector = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.7];
client.search({
collection_name: my_dense_collection,
data: query_vector,
limit: 5,
output_fields: ['pk'],
params: {
nprobe: 10
}
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "my_dense_collection",
"data": [
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.7]
],
"annsField": "dense_vector",
"limit": 5,
"searchParams":{
"params":{"nprobe":10}
},
"outputFields": ["pk"]
}'
## {"code":0,"cost":0,"data":[{"distance":0.55,"id":"453577185629572532","pk":"453577185629572532"},{"distance":0.42,"id":"453577185629572531","pk":"453577185629572531"}]}
類似検索パラメータの詳細については、「基本的なベクトル検索」を参照してください。