疎ベクトル
疎ベクトルは、情報検索や自然言語処理におけるデータ表現の重要な方法です。密ベクトルは、優れた意味理解能力のために人気がありますが、疎ベクトルは、キーワードやフレーズの正確なマッチングが必要なアプリケーションにおいて、より正確な結果を提供することがよくあります。
概要について
疎ベクトルとは、ほとんどの要素がゼロであり、わずかな次元のみが非ゼロ値を持つ高次元ベクトルの特別な表現です。この特性により、疎ベクトルは大規模で高次元であるが疎なデータを処理するのに特に効果的です。一般的なアプリケーションには、次のものがあります:
-
**テキスト分析:**文書を単語の袋ベクトルとして表現し、各次元が単語に対応し、文書に現れる単語のみがゼロ以外の値を持つようにします。
-
**レコメンデーションシステム:**各ディメンションが特定のアイテムに対するユーザーの評価を表し、ほとんどのユーザーがわずかなアイテムしかインタラクションしないユーザーアイテムインタラクション行列。
-
**画像処理:**画像内のキーポイントに焦点を当てた局所的な特徴表現により、高次元の疎ベクトルが生成されます。
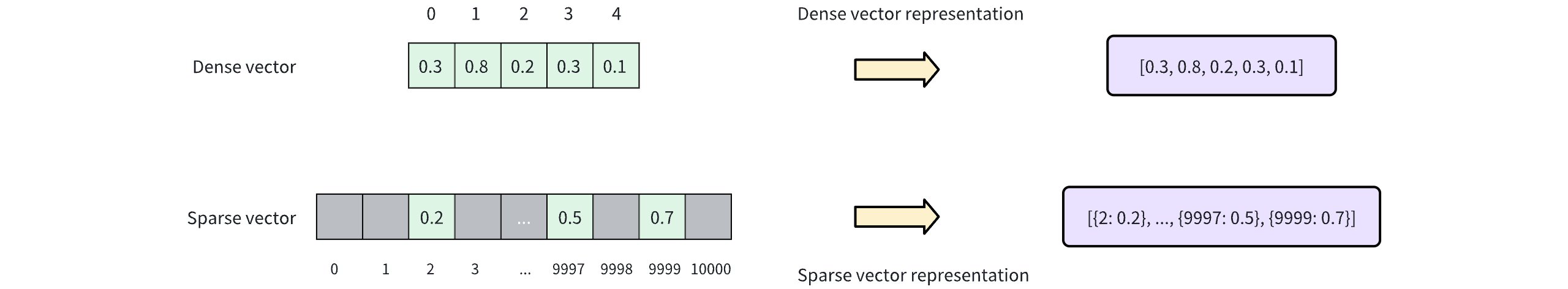
以下の図に示すように、密集ベクトルは通常、各位置に値がある連続配列として表されます(例:[0.3, 0.8、0.2, 0.3, 0.1])。対照的に、疎ベクトルは非ゼロ要素とそのインデックスのみを格納し、しばしばキーと値のペアとして表されます(例:[{2: 0.2}, ..., {9997: 0.5}, {9999:0.7}])。この表現は、特に非常に高次元のデータ(例:10,000次元)を扱う場合に、ストレージスペースを大幅に削減し、計算効率を向上させます。
テキスト処理において、TF-IDF(Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency)やBM25などの様々な手法を用いて、疎ベクトルを生成することができます。また、Zilliz Cloudでは、疎ベクトルの生成や過程を簡単に行うことができます。
テキストデータの場合、Zilliz Cloudは全文検索機能も提供しており、外部の埋め込みモデルを使用してスパースベクトルを生成することなく、生のテキストデータに直接ベクトル検索を実行できます。詳細については、「フルテキスト検索」を参照してください。
ベクトル化後、データは管理とベクトル取得のためにZilliz Cloudに保存できます。以下の図は基本的な過程を示しています。
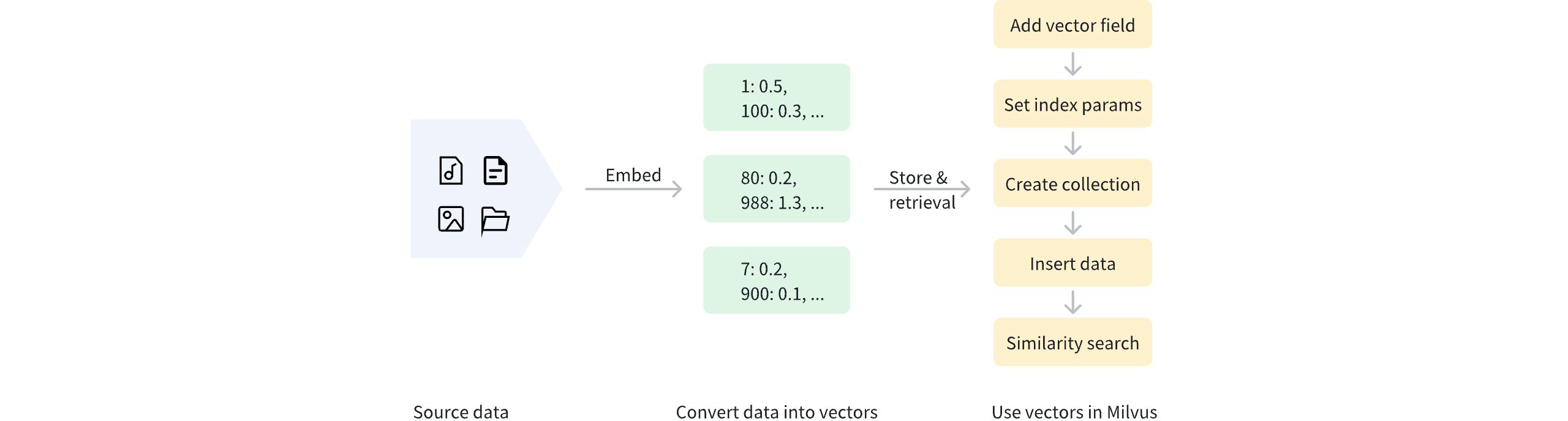
疎ベクトルを使用
Zilliz Cloudは、スパースベクトルを以下のいずれかの形式で表現できます:
-
疎行列(
scipy.sparseクラスを使用)from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
# Create a sparse matrix
row = [0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2]
col = [0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2]
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
sparse_matrix = csr_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape=(3, 3))
# Represent sparse vector using the sparse matrix
sparse_vector = sparse_matrix.getrow(0) -
辞書のリスト(
{dimension_index: value, ...})- Python
- Java
# Represent sparse vector using a dictionary
sparse_vector = [{1: 0.5, 100: 0.3, 500: 0.8, 1024: 0.2, 5000: 0.6}]SortedMap<Long, Float> sparseVector = new TreeMap<>();
sparseVector.put(1L, 0.5f);
sparseVector.put(100L, 0.3f);
sparseVector.put(500L, 0.8f);
sparseVector.put(1024L, 0.2f);
sparseVector.put(5000L, 0.6f); -
タプルイテレータのリスト(
[(dimension_index, value)])# Represent sparse vector using a list of tuples
sparse_vector = [[(1, 0.5), (100, 0.3), (500, 0.8), (1024, 0.2), (5000, 0.6)]]
ベクトルフィールドを追加
スパースベクトルを使用するにはZilliz Cloudクラスタコレクションを作成するときにスパースベクトルを格納するフィールドを定義します。この過程には以下が含まれます:
-
datatypeをサポートされている疎ベクトルデータ型、SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTORに設定します。 -
寸法を指定する必要はありません。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
client = MilvusClient(uri="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
client.drop_collection(collection_name="my_sparse_collection")
schema = client.create_schema(
auto_id=True,
enable_dynamic_fields=True,
)
schema.add_field(field_name="pk", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, is_primary=True, max_length=100)
schema.add_field(field_name="sparse_vector", datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = client.createSchema();
schema.setEnableDynamicField(true);
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("pk")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.maxLength(100)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("sparse_vector")
.dataType(DataType.SparseFloatVector)
.build());
import { DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const schema = [
{
name: "metadata",
data_type: DataType.JSON,
},
{
name: "pk",
data_type: DataType.Int64,
is_primary_key: true,
},
{
name: "sparse_vector",
data_type: DataType.SparseFloatVector,
}
];
export primaryField='{
"fieldName": "pk",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"isPrimary": true,
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 100
}
}'
export vectorField='{
"fieldName": "sparse_vector",
"dataType": "SparseFloatVector"
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": true,
\"fields\": [
$primaryField,
$vectorField
]
}"
この例では、疎ベクトルを格納するためにsparse_vectorという名前のベクトルフィールドが追加されています。このフィールドのデータ型はSPARSE_FLOAT_VECTORです。
ベクトル場のインデックスパラメータを設定する
疎ベクトルのインデックスを作成する過程は、密ベクトルのインデックスと似ていますが、指定されたインデックスタイプ(index_type)、距離メトリック(metric_type)、およびインデックスパラメータ(params)に違いがあります。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse_vector",
index_name="sparse_inverted_index",
index_type="SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX",
metric_type="IP",
params={"inverted_index_algo": "DAAT_MAXSCORE"},
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import java.util.*;
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String,Object> extraParams = new HashMap<>();
extraParams.put("inverted_index_algo": "DAAT_MAXSCORE");
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("sparse_vector")
.indexName("sparse_inverted_index")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.IP)
.extraParams(extraParams)
.build());
const indexParams = await client.createIndex({
index_name: 'sparse_inverted_index',
field_name: 'sparse_vector',
metric_type: MetricType.IP,
index_type: IndexType.SPARSE_WAND,
params: {
inverted_index_algo: 'DAAT_MAXSCORE',
},
});
export indexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "sparse_vector",
"metricType": "IP",
"indexName": "sparse_inverted_index",
"indexType": "SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX",
"params":{"inverted_index_algo": "DAAT_MAXSCORE"}
}
]'
上記の例では:
-
index_type:疎ベクトル場に対して作成するインデックスのタイプ。有効な値:-
SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX:スパースベクトル用の汎用逆インデックス。 -
SPARSE_WAND: Milvus v 2.5.3以前でサポートされていた特殊なインデックス型。📘ノートMilvus2.5.4以降、
SPARSE_WANDは非推奨となっています。その代わりに、互換性を維持しながら等価性を保つために"inverted_index_algo":"DAAT_WAND"を使用することをお勧めします。
-
-
metric_type:疎ベクトル間の類似度を計算するために使用されるメトリック。有効な値:-
IP(内積):ドット積を使用して類似度を測定します。 -
BM 25:通常、テキストの類似性に焦点を当てた全文検索に使用されます。詳細については、Metric TypesとFull Text Searchを参照してください。
-
-
params. inverted_index_algo:インデックスの構築とクエリに使用されるアルゴリズム。有効な値:-
"DAAT_MAXSCORE"(デフォルト):MaxScoreアルゴリズムを使用した最適化されたDocument-at-a-Time(DAAT)クエリ処理。MaxScoreは、最小限の影響を持つ可能性がある用語やドキュメントをスキップすることにより、高k値または多数の用語を持つクエリに対してより良いパフォーマンスを提供します。これは、最大の影響スコアに基づいて用語を必須および非必須グループに分割し、トップkの結果に貢献できる用語に焦点を当てることによって実現されます。 -
「DAAT_WAND」: WANDアルゴリズムを使用した最適化されたDAATクエリ処理。WANDは、最大の影響スコアを活用して非競合ドキュメントをスキップすることで、より少ないヒットドキュメントを評価しますが、ヒットあたりのオーバーヘッドが高くなります。これにより、スキップがより実現可能な小さなk値や短いクエリに対して、WANDはより効率的になります。 -
"TAAT_NAIVE":基本的なTerm-at-a-Time(TAAT)クエリ処理。DAAT_MAXSCOREやDAAT_WANDに比べると遅いですが、TAAT_NAIVEには独自の利点があります。グローバルコレクションパラメータ(avgdl)の変更に関係なく静的なキャッシュされた最大影響スコアを使用するDAATアルゴリズムとは異なり、TAAT_NAIVEはそのような変更に動的に適応します。
-
コレクションを作成
スパースベクトルとインデックスの設定が完了したら、スパースベクトルを含むコレクションを作成できます。以下の例では、create_collectionメソッドを使用してmy_sparse_collectionという名前のコレクションを作成します。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
client.create_collection(
collection_name="my_sparse_collection",
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_sparse_collection")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
import { MilvusClient } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const client = new MilvusClient({
address: 'YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT'
});
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: 'my_sparse_collection',
schema: schema,
index_params: indexParams
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"my_sparse_collection\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $indexParams
}"
データの挿入
コレクションを作成した後、疎ベクトルを含むデータを挿入してください。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
sparse_vectors = [
{"sparse_vector": {1: 0.5, 100: 0.3, 500: 0.8}},
{"sparse_vector": {10: 0.1, 200: 0.7, 1000: 0.9}},
]
client.insert(
collection_name="my_sparse_collection",
data=sparse_vectors
)
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.InsertReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.InsertResp;
List<JsonObject> rows = new ArrayList<>();
Gson gson = new Gson();
{
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
SortedMap<Long, Float> sparse = new TreeMap<>();
sparse.put(1L, 0.5f);
sparse.put(100L, 0.3f);
sparse.put(500L, 0.8f);
row.add("sparse_vector", gson.toJsonTree(sparse));
rows.add(row);
}
{
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
SortedMap<Long, Float> sparse = new TreeMap<>();
sparse.put(10L, 0.1f);
sparse.put(200L, 0.7f);
sparse.put(1000L, 0.9f);
row.add("sparse_vector", gson.toJsonTree(sparse));
rows.add(row);
}
InsertResp insertR = client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_sparse_collection")
.data(rows)
.build());
const data = [
{ sparse_vector: { "1": 0.5, "100": 0.3, "500": 0.8 } },
{ sparse_vector: { "10": 0.1, "200": 0.7, "1000": 0.9 } },
];
client.insert({
collection_name: "my_sparse_collection",
data: data,
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"data": [
{"sparse_vector": {"1": 0.5, "100": 0.3, "500": 0.8}},
{"sparse_vector": {"10": 0.1, "200": 0.7, "1000": 0.9}}
],
"collectionName": "my_sparse_collection"
}'
## {"code":0,"cost":0,"data":{"insertCount":2,"insertIds":["453577185629572534","453577185629572535"]}}
類似検索を行う
疎ベクトルを使用して類似検索を行うには、クエリベクトルと検索パラメータを準備してください。
# Prepare search parameters
search_params = {
"params": {"drop_ratio_search": 0.2}, # Additional optional search parameters
}
# Prepare the query vector
query_vector = [{1: 0.2, 50: 0.4, 1000: 0.7}]
この例では、drop_ratio_searchはスパースベクトル専用のオプションパラメータであり、検索中にクエリベクトル内の小さな値を微調整することができます。例えば、{"drop_ratio_search": 0.2}の場合、クエリベクトル内の最小20%の値は検索中に無視されます。
次に、searchメソッドを使用して類似検索を実行します。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- cURL
res = client.search(
collection_name="my_sparse_collection",
data=query_vector,
limit=3,
output_fields=["pk"],
search_params=search_params,
)
print(res)
# Output
# data: ["[{'id': '453718927992172266', 'distance': 0.6299999952316284, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172266'}}, {'id': '453718927992172265', 'distance': 0.10000000149011612, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172265'}}]"]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.SparseFloatVec;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
Map<String,Object> searchParams = new HashMap<>();
searchParams.put("drop_ratio_search", 0.2);
SortedMap<Long, Float> sparse = new TreeMap<>();
sparse.put(10L, 0.1f);
sparse.put(200L, 0.7f);
sparse.put(1000L, 0.9f);
SparseFloatVec queryVector = new SparseFloatVec(sparse);
SearchResp searchR = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_sparse_collection")
.data(Collections.singletonList(queryVector))
.annsField("sparse_vector")
.searchParams(searchParams)
.topK(3)
.outputFields(Collections.singletonList("pk"))
.build());
System.out.println(searchR.getSearchResults());
// Output
//
// [[SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536759}, score=1.31, id=453444327741536759), SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536756}, score=1.31, id=453444327741536756), SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=453444327741536753}, score=1.31, id=453444327741536753)]]
await client.search({
collection_name: 'my_sparse_collection',
data: {1: 0.2, 50: 0.4, 1000: 0.7},
limit: 3,
output_fields: ['pk'],
params: {
drop_ratio_search: 0.2
}
});
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "my_sparse_collection",
"data": [
{"1": 0.2, "50": 0.4, "1000": 0.7}
],
"annsField": "sparse_vector",
"limit": 3,
"searchParams":{
"params":{"drop_ratio_search": 0.2}
},
"outputFields": ["pk"]
}'
## {"code":0,"cost":0,"data":[{"distance":0.63,"id":"453577185629572535","pk":"453577185629572535"},{"distance":0.1,"id":"453577185629572534","pk":"453577185629572534"}]}
類似検索パラメータの詳細については、「基本的なベクトル検索」を参照してください。